Table 4.
Test of reproductive isolation between strains from the three C. sesamiae lineages and C. flavipes using cross-mating experiments
| Mating occurrence |
Mating traits |
Parasitic devpt. |
Progeny traits |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (♀ × ♂) | nobs | % couples mating | nmated | Latency | Duration | nhosts | % cocoon clusters | ncluster | Size (no. of cocoons) | Nymphal mortal. (%) | Sex ratio (%♀) | Resulting net reprod. rate |
| A. Crosses between Cs Typha strain (lineage 2) and Cs Mombasa strain (lineage 3) | ||||||||||||
| T × T | 30 | 77 a | 23 | 472 (113) ab | 21 (1) a | 20 | 80 | 16 | 52 (9) | 9 (3) | 47 (9) a | 10 (3) a |
| M × M | 60 | 33 b | 20 | 536 (177) ab | 23 (4) a | 20 | 90 | 18 | 50 (5) | 11 (6) | 74 (7) a | 9.5 (2) a |
| M × T | 56 | 16 b | 9 | 74 (28) b | 23 (3) ab | 9 | 89 | 8 | 58 (7) | 7 (4) | 0.005 (0) b | 0.05 (0.04) b |
| T × M | 38 | 66 a | 25 | 660 111) a | 41 (5) b | 14 | 71 | 10 | 48 (11) | 14 (6) | 37 (12) a | 5 (3) a |
| analysis |
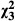 = 36.62
P
<10−4
= 36.62
P
<10−4
|
K3 = 9.82 P =0.020 | K3 = 13.38 P =0.004 | Fisher test P = 1, NS | K3 = 1.06 NS | K3 = 3.36 NS | K3=21.21 P <10−4 | K3=16.88 P =10−3 | ||||
| TM × T | 53 | 51 | 27 | 234 (89) | 16 (1) | 10/17 | 0/23.5 | 4 | 2.5 (0.3) | 54 (16) | 100 | 0/0.15 |
| TM × M | 67 | 72 | 48 | 474 (77) | 28 (2) | 11/24 | 0/68 | 16 | 11 (2) | 33 (9) | 99 | 0/4.5 |
| B. Crosses between Cs Typha strain and Cs Kitale strain (lineage 1) | ||||||||||||
| T × T | 34 | 59 a | 20 | 536 (154) | 22 (1) a | 17 | 71 | 12 | 62 (7) ab | 16 (7) | 43 (9) a | 9 (2) a |
| K × K | 29 | 69 a | 20 | 383 (104) | 18 (1) a | 19 | 58 | 11 | 53 (7) a | 6 (3) | 67 (8) a | 14 (3) a |
| K × T | 30 | 0 b | 0 | /// | /// | /// | /// | /// | /// | /// | /// | 0 |
| T × K | 31 | 84 a | 26 | 631 (144) | 57 (5) b | 21 | 48 | 10 | 84 (10) b | 8 (6) | 3.3 (2) b | 1 (0.6) b |
| analysis |
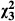 = 49.15
P
<10−4
= 49.15
P
<10−4
|
K2 = 0.75 NS | K2= 36.70 P <10−4 |
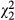 = 2.03 NS = 2.03 NS |
K2 = 7.05 P =0.03 | K2 = 3.28 NS | K2=18.81 P <10−4 | K2=15.63 P <10−3 | ||||
| TK × T | 48 | 75 | 36 | 284 (60) | 17 (1) | 13/15 | 0/7 | 1 | 4 | 100 | /// | 0 |
| TK × K | 35 | 94 | 33 | 284 (68) | 56 (6) | 15/9 | 7/11 | 1/1 | 18/1 | 17/0 | 100/100 | 1/0.1 |
| C. Crosses between Cs Typha strain and C. flavipes | ||||||||||||
| T × T | 124 | 60 a | 75 | 427 (36) c | 24 (1) b | 48 | 63 | 30 | 33 (2) ab | 11 (1) a | 54 (5) b | 6 (1) a |
| Cf × Cf | 112 | 62 a | 69 | 201 (25) a | 18 (1) a | 55 | 42 | 23 | 40 (4) a | 7 (2) a | 80 (6) a | 8 (1) a |
| T × Cf | 50 | 72 a | 36 | 384 (83) ab | 43 (5) c | 28 | 43 | 12 | 26 (4) b | 12 (2) a | 0 (0) c | 0 (0) b |
| Cf × T | 163 | 7 b | 12 | 458 (93) bc | 14 (2) a | 12 | 42 | 5 | 37 (5) ab | 7 (2) a | 0 (0) c | 0 (0) b |
| Analysis |
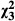 = 133
P
<10−4
= 133
P
<10−4
|
K3 = 35.72 P <10−4 | K2 = 105.3 P <10−4 |
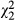 = 5.32 NS = 5.32 NS |
K3 = 8.05 P = 0.045 | K3 = 8.08 P = 0.045 | K3=43.10 P <10−4 | K3=33.81 P <10−4 | ||||
T, Cs Typha strain; M, Cs Mombasa strain; K, Cs Kitale strain; TK, hybrid daughters from T mother and K father; TM, daughters from T mother and M father; n, sample size.
See Materials and methods for significance of traits and statistical analyses.
Mean values and standard errors (in brackets) are given for each trait. Gray highlight is values indicating reproductive barriers. Parental females were tested on their developmental host, S. nonagrioides for Cs Typha, and S. calamistis for Cs Kitale and Mombasa. Hybrid females were tested on S. nonagrioides and S. calamistis (left/right, respectively). Letters indicate significant difference at P < 0.05. Statistical results are in bold when significant.
