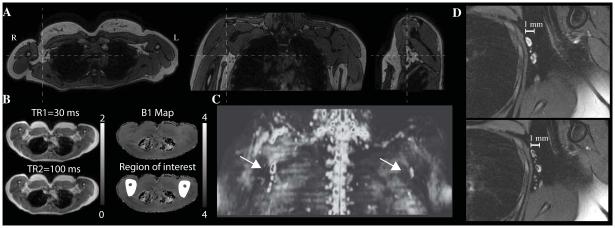
Figure 1. Spatial coverage and planning of lymphatic imaging.
(A) Orthogonal representations of 3D T2-weighted mDIXON scans, which are used for identifying the approximate location of axillary lymph nodes and surrounding muscle and fat structure. (B) Multi-TR B1 maps for one control subjectshowing typical B1 consistency between right and left arms. In the bottom right panel, an example region-of-interest (ROI) used for amide proton transfer (APT) analysis is shown (white). (C) The 3D Diffusion Weighted Imaging with Background Suppression (DWIBS) scan (maximum intensity projection) demarcates the approximate location of axillary lymph nodes, and (E) the high spatial resolution fat-suppressed T2-weighted scans highlights structural characteristics of the lymph nodes. These images can be acquired non-invasively using standard MRI hardware in less than 10 min, and can be used for guiding assessment of functional changes in human lymphatics.