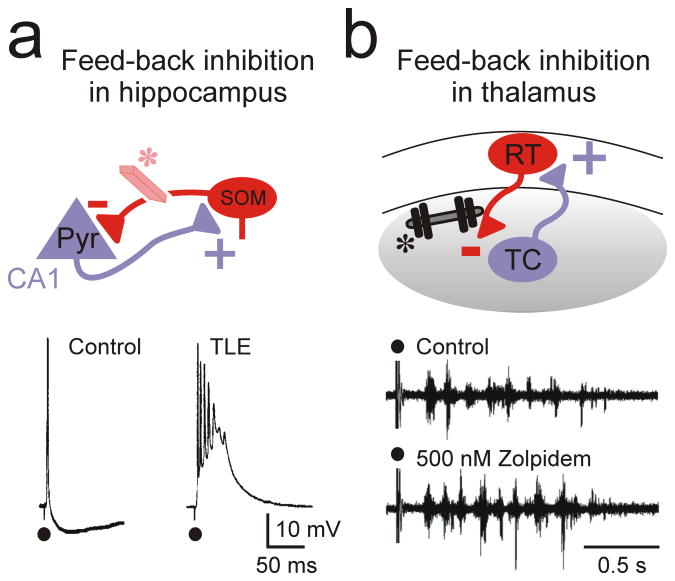
Figure 3. Feed-back inhibition in cortical and thalamic microcircuits.
(a) In the cortex, inhibitory SOM interneurons provide a feed-back inhibition to pyramidal neurons that excite them. Loss of this inhibition (eraser*) has been implicated in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE)37. (b) In the somatosensory thalamus, inhibitory interneurons provide a robust feed-back inhibition to TC neurons that excite them. Increasing this feed-back inhibition (dumbbell weight *) by Zolpidem, or by clonazepam in α3H126R mice (not shown69), which specifically affects RT-TC but not RT-RT connections, enhances epileptiform oscillations. Pyr, pyramidal; SOM, somatostatin-positive; RT, reticular thalamic neuron; TC, thalamocortical neuron.