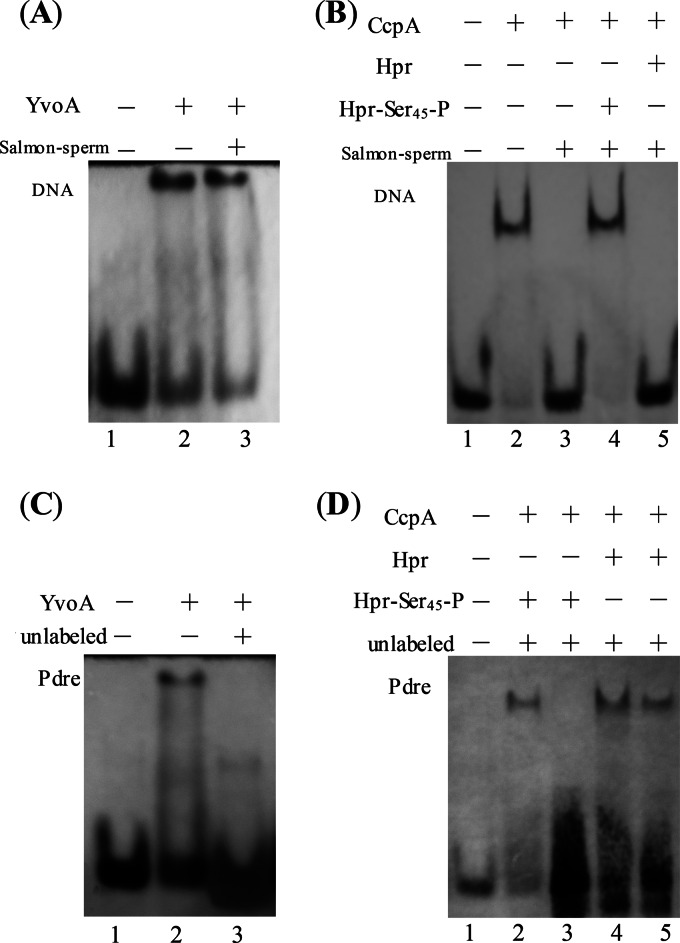
FIG 4.
EMSAs to determine specific binding of YvoABt and CcpABt to drechiB and crechiB. DNA fragments were detected by using a biotin chromogenic reagent. (A and C) Nonspecific and specific competition assays with YvoABt (0.5 μM) and Pdre (0.1 μM) (40 bp). (A) Lane 1, Pdre (biotin-labeled DNA [Bio]); lane 2, Pdre (Bio) and YvoABt; lane 3, Pdre (Bio), YvoABt, and 0.5 ng μl−1 salmon sperm DNA. (C) Lane 1, Pdre (Bio); lane 2, Pdre (Bio) and YvoABt; lane 3, Pdre (Bio), YvoABt, and a 100-fold excess of unlabeled Pdre. (B and D) Nonspecific and specific competition assays with CcpABt (0.5 μM) and Pcre (0.1 μM). (B) Lane 1, Pcre (Bio); lane 2, Pcre (Bio) and CcpABt; lane 3, Pcre (Bio), CcpABt, and 0.5 ng μl−1 salmon sperm DNA; lanes 4 and 5, Pcre (Bio), CcpABt, and 0.5 ng μl−1 salmon sperm DNA plus 2 μM Hpr and 2 μM Hpr-Ser45-P, respectively. (D) Lane 1, Pcre (Bio); lanes 2 and 3, Pcre (Bio), CcpABt, and Hpr-Ser45-P plus 150- and 300-fold excesses of unlabeled Pcre, respectively; lanes 4 and 5, Pcre (Bio), CcpABt, and Hpr plus 150- and 300-fold excesses of unlabeled Pcre, respectively.