FIG 2.
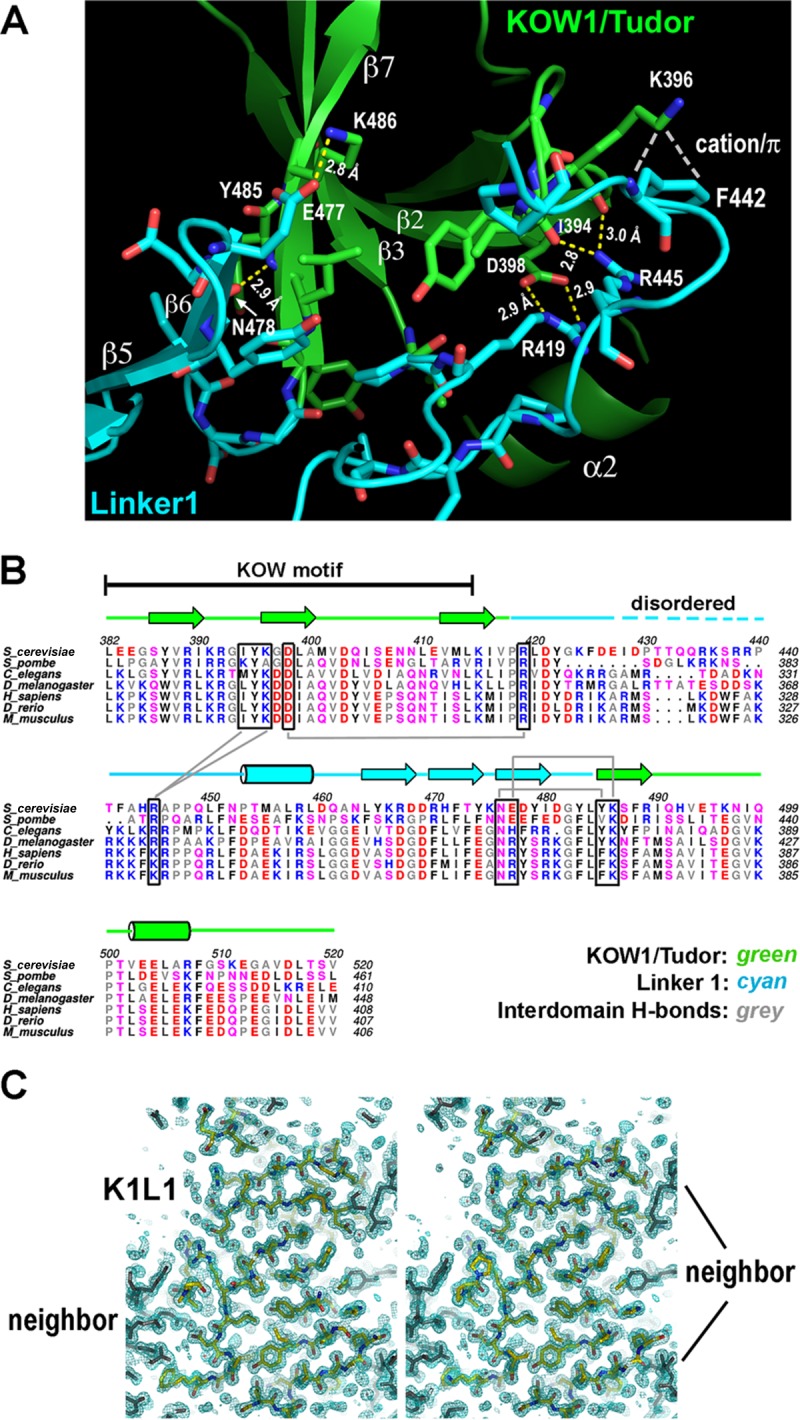
K1L1 forms a rigid-body structure with a flexible segment. (A) An extensive interface between the KOW1-Tudor and Linker1 lobes. Hydrogen bonds between K1 and L1 residues are shown with yellow dashed lines, a cation-π electron interaction is shown with white dashes, and van der Waals interactions are not shown. The interface buries a total of 1,145 Å2 of solvent-accessible surface. (B) Conservation of hydrogen bond-forming residues (boxed) in the interface. Secondary-structural elements are shown above the multiple aligned eukaryotic sequences, and the interdomain hydrogen bonds are indicated with gray lines. Basic, blue; acidic, red; polar, pink; hydrophobic, gray and black. (C) The K1L1 electron density at 1.09 Å (2Fo-Fc omit map contoured at 1.0 σ [green mesh; Fo, observed structure factor amplitudes; Fc, calculated structure factor amplitudes; omit map, model-omitted electron density map; σ, standard deviation of electron density]) is of high quality. Shown is a stereo plot of a slab through the middle of the structure. The K1L1 model is colored by atom type, and neighboring molecules in the crystal lattice are colored gray. Atomic features, such as phenol rings and carbonyl groups (red), are resolved.
