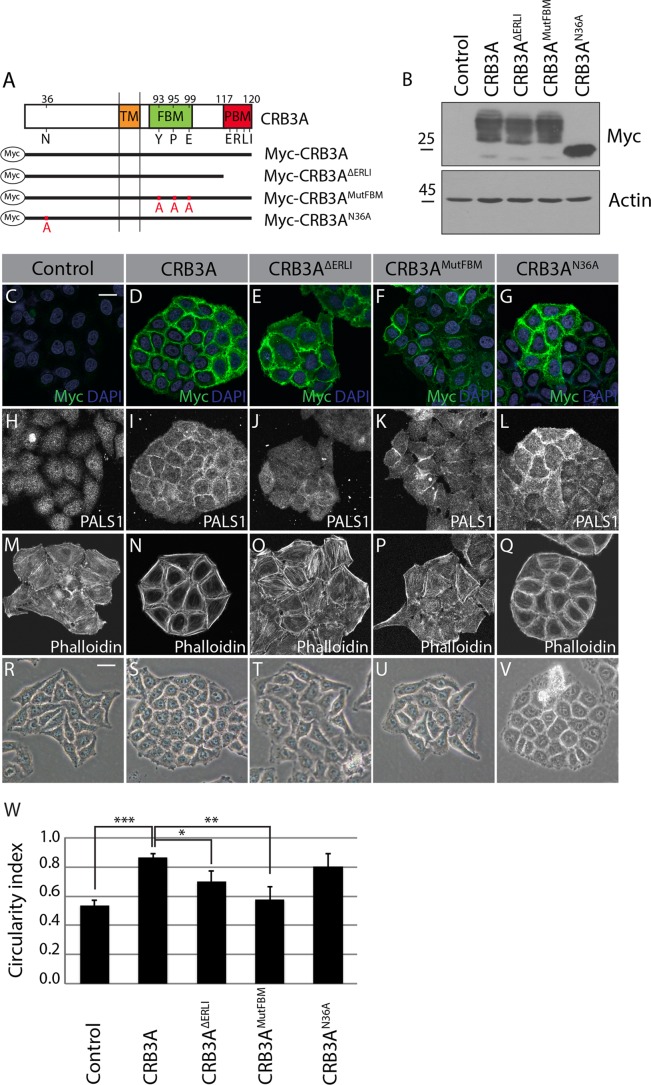
FIG 2.
The CRB3A-dependent reorganization of the cytoskeleton requires both the FBM and PBM. (A) Schematics of the truncated or mutated Myc-tagged CRB3A proteins used for the structure-function analysis. Myc-CRB3AΔERLI lacks the PBM, Myc-CRB3AMutFBM contains a mutated FBM (Y93A, P95A, and E99A), and Myc-CRB3AN36A contains a mutated N-glycosylation site (N36A). Numbers indicate amino acid positions in CRB3A sequence. TM, transmembrane domain. (B) Western blotting using an anti-Myc antibody showing the relative expression of Myc-CRB3A mutant proteins in HeLa cells. Control cells were transfected with the empty MFGi vector. (C to G) Myc-tag immunostaining performed on control HeLa cells (empty vector) or HeLa cells expressing wild-type Myc-CRB3A or one of the mutant Myc-CRB3A proteins depicted in panel A. (H to L) Immunofluorescence of PALS1 in control HeLa cells (empty vector) or HeLa cells expressing Myc-CRB3A, Myc-CRB3AΔERLI, Myc-CRB3AMutFBM, or Myc-CRB3AN36A. (M to Q) F-actin staining using phalloidin in control HeLa cells (empty vector) or HeLa cells expressing Myc-CRB3A, Myc-CRB3AΔERLI, Myc-CRB3AMutFBM, or Myc-CRB3AN36A. (R to V) Phase-contrast images of control HeLa cells (empty vector) or HeLa cells expressing Myc-CRB3A, Myc-CRB3AΔERLI, Myc-CRB3AMutFBM, or Myc-CRB3AN36A. (W) Histogram showing the circularity indexes of the colonies formed by the cell lines shown in panels R to V. Bars represent means ± standard deviations (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). Scale bars, 20 μm (C) and 30 μm (R).