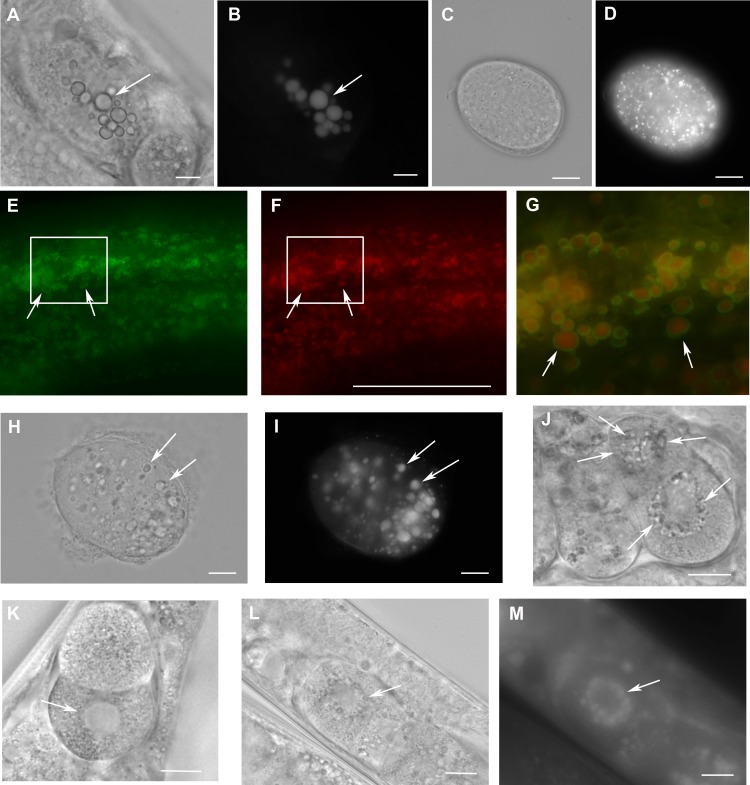
Figure 4. Loss of W01A8.1 function results in abnormal lipid droplet appearance.
(A) and (B) An embryo from a hermaphrodite inhibited for W01A8.1 function by RNAi. Large lipid droplets stained by LipidTox (B) are visible also in Nomarski optics (A) in contrast with a control embryo that has only small and more evenly distributed lipid droplets (C—Nomarski optics and D—LipidTox staining). (E–J, L) and (M) Images of structures observed in animals with disrupted W01A8.1. (E) and (F) show structures with the appearance of lipid droplets in the intestine of an animal with disrupted W01A8.1 balanced with the synthetic transgene W01A8.1(synth)::gfp. GFP tagged synthetic W01A8.1a is localized on lipid droplets-like vesicular structures (E). (F) Shows the same area stained with LipidTox. (G) Shows in magnification a merged image of the area indicated by white rectangles in (E) and (F). Arrows indicate W01A8.1(synth)::GFP labeled lipid droplets (green) positive for lipids in LipidTox staining (red). (H) and (I) show an embryo of a parent with disrupted W01A8.1 that had confirmed loss of the balancing transgene. Large LipidTox stained droplets are visible in Nomarski optics (H) as well as in LipidTox staining (I). Their enlargement is clearly visible in comparison with the wild type embryo shown in (C) and (D). (J) and (K) are images of live animals. (J) Shows an embryo with disrupted W01A8.1 and confirmed loss of the balancing transgene. Large vesicular structures are formed around the dividing nucleus (arrows). (K) Shows a control embryo with normal appearance of the nuclear periphery (arrow). (L) and (M) show a one cell embryo from a parent with disrupted W01A8.1 and confirmed loss of extrachromosomal array containing W01A8.1(a)synth::gfp after fixation and staining by LipidTox with large lipid droplets around the dividing nucleus visible in Nomarski optics (L) and positive for lipids in LipidTox staing (M) indicated by arrows. Bars represent 10 µm.