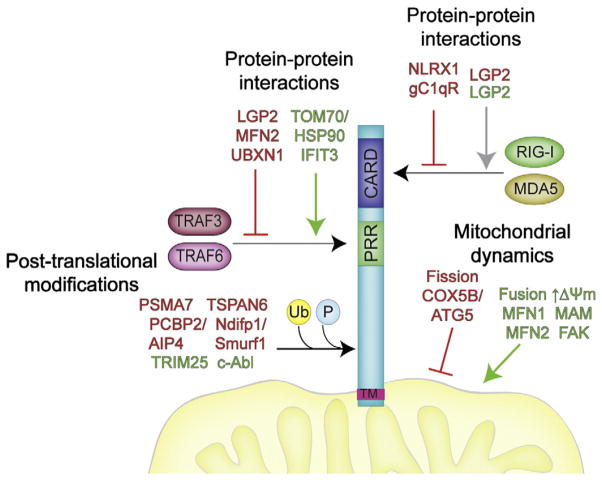
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms of MAVS regulation. There are multiple mechanisms by which MAVS is regulated to exert cellular control over innate immune signaling. MAVS can be regulated by host cell factors that inhibit MAVS signaling by direct protein–protein interactions, by altering mitochondrial properties or dynamics, or by post-translational modifications. PRR, proline-rich region; Ub, ubiquitination; P, phosphorylation. Positive regulators of MAVS signaling are shown in green text and negative regulators of MAVS signaling are shown in red text. Note that LGP2 is shown in both red and green given conflicting results on its role in the regulation of RLR signaling.