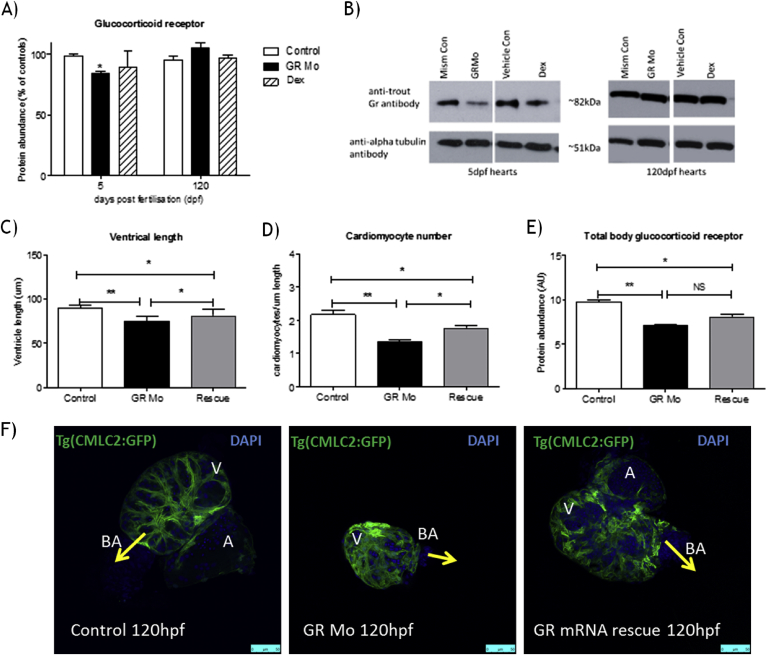
Fig. 3.
Effects of glucocorticoid receptor morpholino and rescue on the embryonic heart Western blot analysis was carried out to determine whether glucocorticoid receptor protein (Gr) was reduced in isolated hearts from zebrafish embryos (5 days post fertilization (5 dpf)) or adults (120 dpf) which had been treated with either glucocorticoid receptor (GR) translational blocking morpholino (GR Mo) or with GR agonist dexamethasone (Dex) [100 μM] for 120 h (5 dpf). A) Densitometry of Western blots of Gr abundance in isolated hearts. Data are n = 3 (150 embryo heart or 10 adult hearts per n), given as a mean percentage of their respective controls (mism Mo for GR Mo and vehicle for Dex) ± SEM analysed by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. *p ≤ 0.05. B) Example of Western blot of embryonic (5 dfp) and adult (120 dpf) heart tissue lysates probed with antibodies against Gr with alpha-tubulin (loading control), C) Success of GR Mo was further determined following co-injection of rescue mRNA with GR Mo and calculation of ventricle length at 120 h post fertilization (hpf) D) Calculation of cardiomyocyte number at 120 hpf. C and D) n = 3 (6 embryos per group). Data are mean ± SEM analysed by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test vs each individual group. *p ≤ 0.05 and **p ≤ 0.01. E) Densitometry of Western blots of Gr abundance in 120 hpf whole embryo homogenate. Data are n = 3 (10 embryo per n), data given as relative protein abundance for control (mism Mo), GR Mo, and Gr mRNA rescue (rescue) n = 3 mean ± SEM analysed by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test, *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01. F) Confocal images of isolated 120 hpf Tg (CMLC2: GFP) zebrafish hearts (green) co-stained with DAPI nuclear stain (blue), images are isolated from embryos which were treated with control morpholino (mism Mo), GR Mo and capped GR mRNA (rescue) co-injected with GR Mo. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)