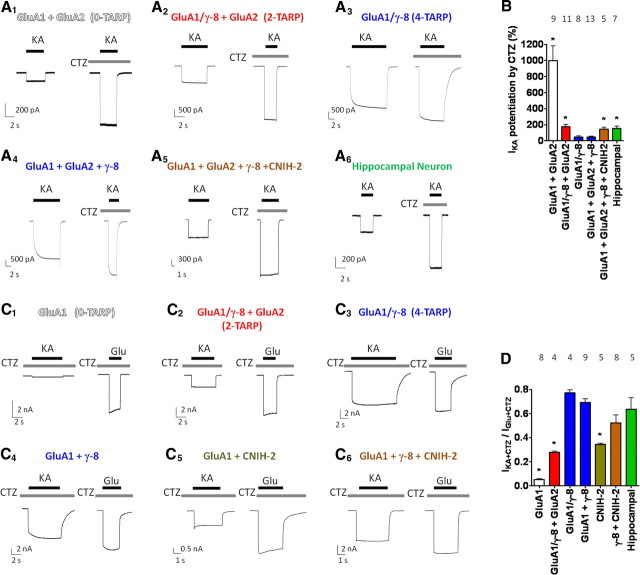
Figure 3.
AMPA receptors coexpressing reduced γ-8 with CNIH-2 exhibit CA1 hippocampal neuron-like kainate/cyclothiazide pharmacology. A1–A6, Representative traces of kainate-evoked currents (±CTZ) from HEK 293T cells cotransfected with GluA1 plus GluA2 alone (A1), GluA1/γ-8 plus GluA2 (A2; two TARPs), GluA1/γ-8 (A3; four TARPs), GluA1 plus GluA2 plus γ-8 (A4), GluA1 plus GluA2 plus γ-8 plus CNIH-2 (A5), and from acutely isolated CA1 hippocampal neurons (A6). B, Quantification of CTZ potentiation of kainate-evoked currents reveals that reducing the number of γ-8 per AMPA receptor complex mimics the magnitude of CTZ potentiation observed in native CA1 hippocampal AMPA receptors. C1–C6, Representative traces of both kainate-evoked and glutamate-evoked currents in the presence of CTZ from HEK 293T cells transfected with GluA1 alone (C1), tandem GluA1/γ-8 plus GluA2 (C2; two TARPs), tandem GluA1/γ-8 (C3; four TARPs), nontethered GluA1 plus γ-8 (C4), GluA1 plus CNIH-2 (C5), or GluA1 plus γ-8 plus CNIH-2 (C6). D, Reducing the number of γ-8 subunits per AMPA receptor complex decreases IKA+CTZ/IGlu+CTZ, whereas coexpression of CNIH-2 with GluA1 plus γ-8 maintains a high IKA+CTZ/IGlu+CTZ ratio. Note that GluA1 plus CNIH-2 shows a higher IKA+CTZ/IGlu+CTZ ratio than GluA1 alone and that GluA1 plus γ-8 plus CNIH-2 more closely resembles the CA1 hippocampal phenotype than two-TARP γ-8 AMPA receptors. *p < 0.05 using Fisher's least significant difference (LSD) when compared with GluA1 plus GluA2 plus γ-8 (B) or GluA1 plus γ-8 (D). Numbers of repetitions are indicated above the bar graphs. Summary data are mean ± SEM.