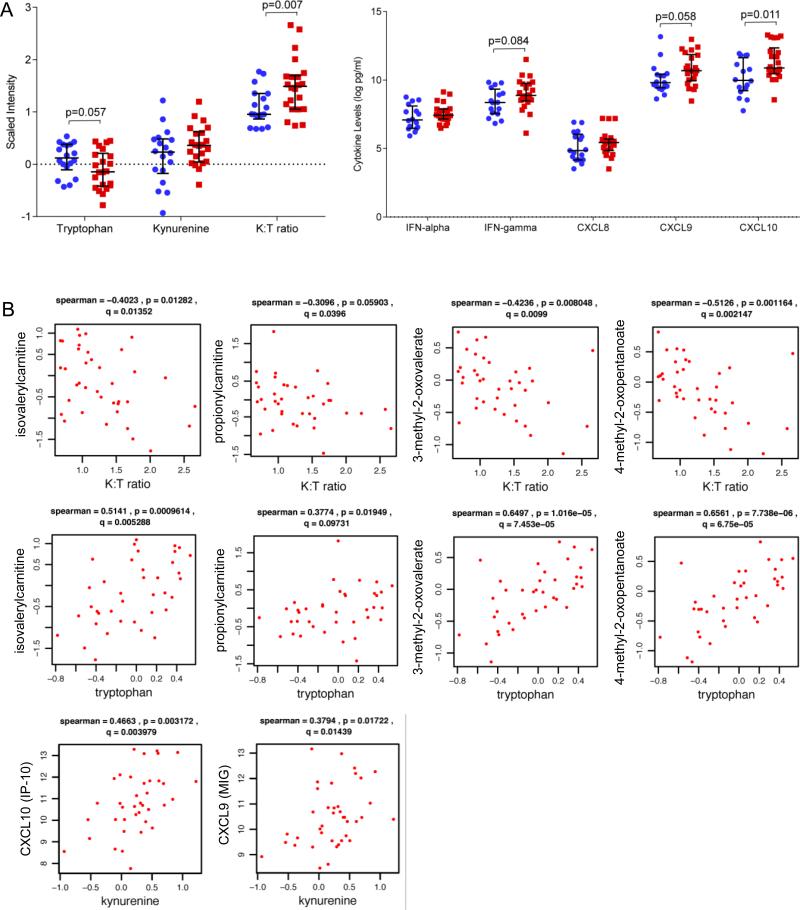
Figure 3. Depressive symptoms are associated with augmented IFN responses and increased tryptophan catabolism in HIV patients.
A) Beeswarm plots of tryptophan catabolism metabolites and inflammation markers altered in HIV patients with (n=20, red) vs. without depressive symptoms (n=20, blue) from the merged HIV dataset (n=40, age<50 years old). HIV-positive subjects with versus without depressive symptoms were matched for age, race, gender, stage of disease (current and nadir CD4), HIV plasma viral load, and ART use. Medians are represented by horizontal bars and error bars represent IQR. P-values were calculated using Mann Whitney U test. B) Correlation plots of markers of tryptophan catabolism, IFN responses (IFN-gamma-induced chemokines CXCL9/MIG and CXCL10/IP-10), and metabolites associated with depressive symptoms in the merged HIV dataset (n=40). Spearman correlations were used to examine relationships between IFN-gamma-induced chemokines and metabolite levels. The correlation coefficient R, and p-value are shown above each plot.