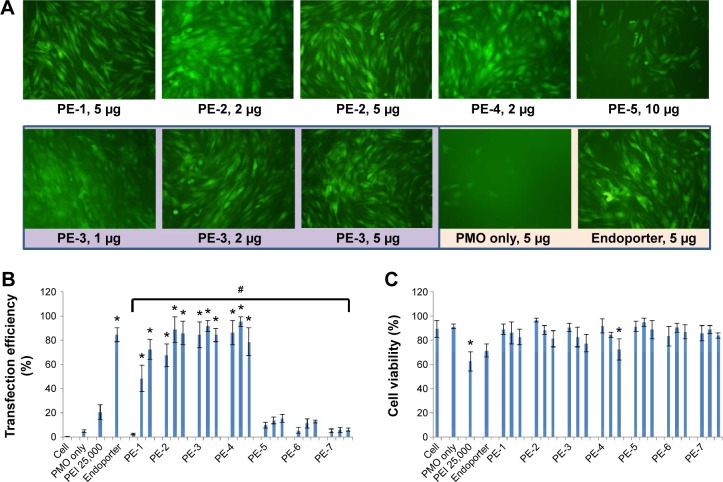
Figure 3.
Delivery efficiency and toxicity of PMOE50/PE complexes in a C2C12E50 cell line determined by fluorescence microscopy and fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis.
Notes: (A) Representative fluorescence images of PMO-induced exon-skipping in the C2C12E50 cell line. The images were taken 48 hours after treatment. Original magnification, 100×. (B) Transfection efficiency of PMO formulated with PEs (one-way analysis of variance test, #P≤0.05 indicates a significant difference between PE groups; Student’s t-test, *P≤0.05 compared with PMO only). (C) Cell viability (one-way analysis of variance test, P=0.585, no significant difference between PE groups was found; Student’s t-test, *P≤0.05 compared with untreated cells). In this test, 5 µg of PMOE50 were formulated with PEs (1, 2, 5 µg), and PEI 25,000 (2 µg), and Endoporter (5 µg) was formulated as the control in 0.5 mL of 10% fetal bovine serum-Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium, respectively. The results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, in triplicate.
Abbreviations: PEs, polyelectrolytes; PEI, polyethylenimine; PMO, phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer.