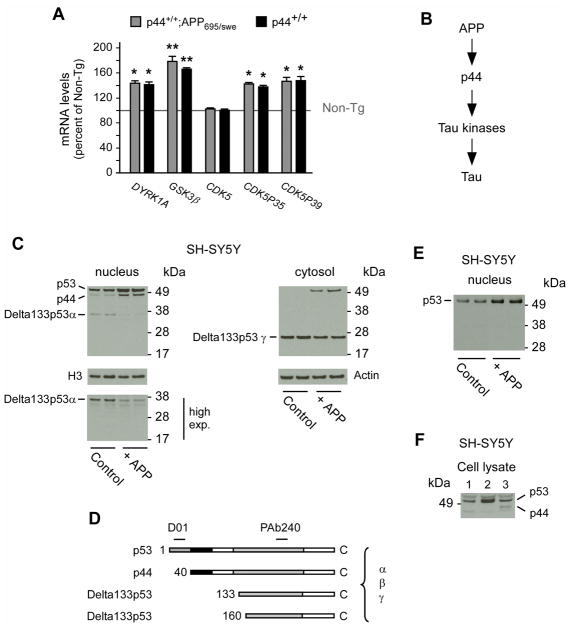
Fig. 1. APP can induce the expression of p44.
(A) Quantitative real-time PCR determination of indicated kinases in the hippocampal formation. Animals (males) were 2.5-month-old when analyzed. All values are mean (n=5) ± sd. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005. (B) Schematic view showing APP upstream of p44. (C) Western blot analysis showing induction of p44 as a result of APP overexpression. A longer exposure of the membrane (high exp.) is included to show the down-regulation of Delta133p53α. The nuclear marker H3 was used as loading control. (D) Schematic view of p53 isoforms showing the domains targeted by D01 and PAb240 antibodies. (E) The nuclear fraction probed with PAb240 in (C) was probed again with D01. (F) Western blot showing migration profile of p53 and p44 following transfection in SH-SY5Y cells. Lane 1, empty vector; lane 2, p53 cDNA; lane 3, p44 cDNA.