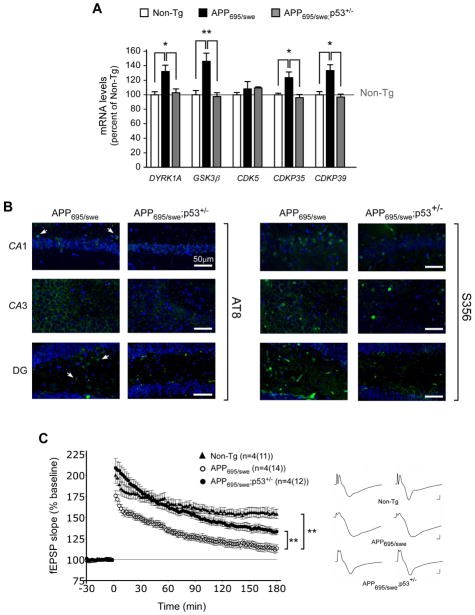
Fig. 5. Haploinsufficiency of p53/p44 can rescue some of the phenotypic features caused by the overexpression of APP in the mouse.
(A) Quantitative real-time PCR determination of indicated kinases in the hippocampal formation. Animals (males) were 2.5-month-old when analyzed. All values are mean (n=12) ± sd. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005. (B) Immunostaining with anti-phospho-tau antibodies shows reduced labeling in APP695/swe;p53+/− mice. Two different antibodies were used: AT8 (against pSer202 and pThr205) and S356 (against pSer356). Mice (males) were ~1-year-old when analyzed. (C) Long-term potentiation (LTP) induction in hippocampal slices. Mice (males) were 2.5-month-old when analyzed. APP695/swe mice display deficits in the late component of LTP. These deficits are rescued by p53/p44 haploinsufficiency. **p < 0.005.