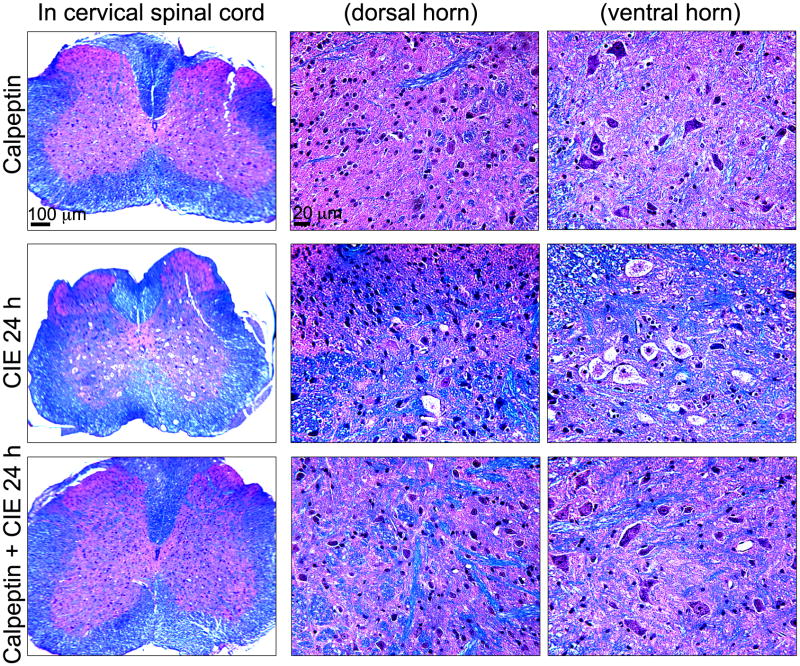
Fig. 6.
Neuroprotective efficacies of calpeptin following CIE exposure and withdrawal. Coronal slices (8 μm) from cervical spinal cord were stained with LFB and counterstained with H&E; myelin was stained as blue-green color and gray matter as pink. Images represent LFB staining in spinal cord slices from 3 experimental groups (n = 3): calpeptin (as drug control), CIE 24 h (withdrawal), and calpeptin + CIE 24 h (mice received calpeptin before each EtOH vapor inhalation). In 1st column, low magnification images (40 ×) are presented, which are magnified (200 ×) in the next two columns at dorsal horn and ventral horn respectively. Calpeptin control group showed normal sensory neurons at dorsal horn and motoneurons at ventral horn respectively (upper panel). In CIE 24h spinal cord sections prominent chromatolysis-like changes were seen in the motoneuron (middle panel), which were significantly attenuated with calpeptin-pre-treatment (lower panel).