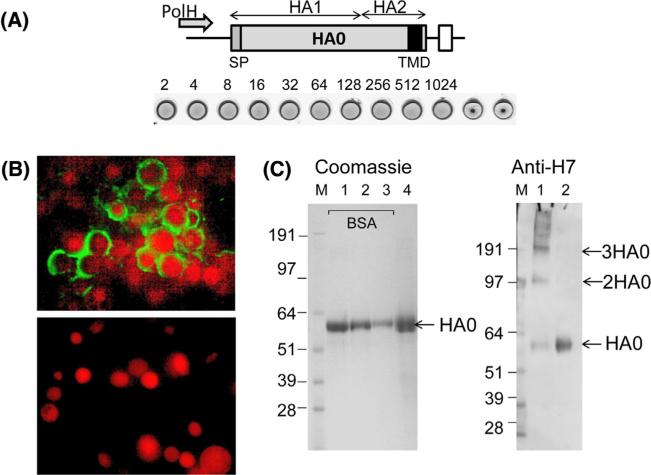
Fig. 1.
Expression and characterization of rH7 SVP. (A) Expression cassette for rH7 gene. Indicated are locations of baculovirus polyhedrin promoter (PolH), locations of HA1 and HA2 within rH7 HA0 protein, RNA transcription termination signal (open box), signal peptide (SP) and transmembrane domain (TMD) within rH7 (filled box). Hemagglutination assay of purified rH7 protein using 1% turkey red blood cells is also shown. Dilutions are indicated. (B) Immunofluorescence assay (IFA) of Sf9 cells infected with rH7-expressing recombinant baculovirus (upper panel), and of uninfected control Sf9 cells (bottom panel). Cell nuclei were counterstained using propidium iodide. (C) Left panel: SDS-PAGE stained with GelCode Blue stain; lanes 1, 2, 3, and 4 show 1.5, 1.0 and 0.5 μg BSA, as well as 3.0 μg rH7, respectively. Right panel: western blot using H7 antiserum; lane 1 shows rH7 after cross-linking with glutaraldehyde; lane 2 shows purified rH7. M, SeeBlue Plus2 marker (Life Technologies). Western blot was done using chicken H7N3 virus-specific antibody at 1:100 dilution.