Figure 3. Comparison of oxygen consumption rates (OCR) and extracellular acidification rates (ECAR) in synaptosomal mitochondria derived from the striatum (ST) and mediobasal hypothalamus (MBH).
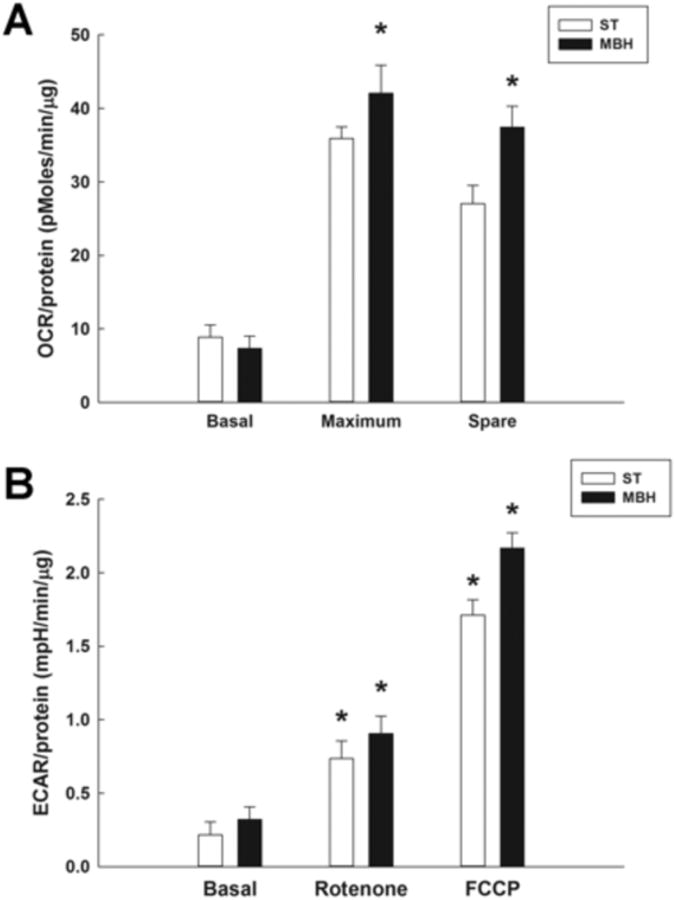
OCR and ECAR measurements were performed using a Seahorse XF24 analyzer, with 20 μg of synaptosomal protein derived from each region yielding a respiratory control ratio' (RCR') of greater than 3. A; OCR (pmoles/min/μg) of ST- and MBH-derived synaptosomal mitochondria during basal, maximum and spare aerobic respiration measured using a Seahorse XF analyzer. Columns represent mean OCR of synaptosomal mitochondria and vertical lines + 1 SEM of determinations in 5 mice. * indicates OCR of maximum and spare respiration in MBH that are significantly different (p < 0.05) from those in ST. B; ECAR (mpH/min/μg) of ST- and MBH-derived synaptosomal mitochondria under basal conditions, and following inhibition (rotenone) or uncoupling (FCCP) of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. * indicates ECAR in FCCP- and rotenone-treated groups that are significantly different (p < 0.05) from basal ECAR values for each region.
