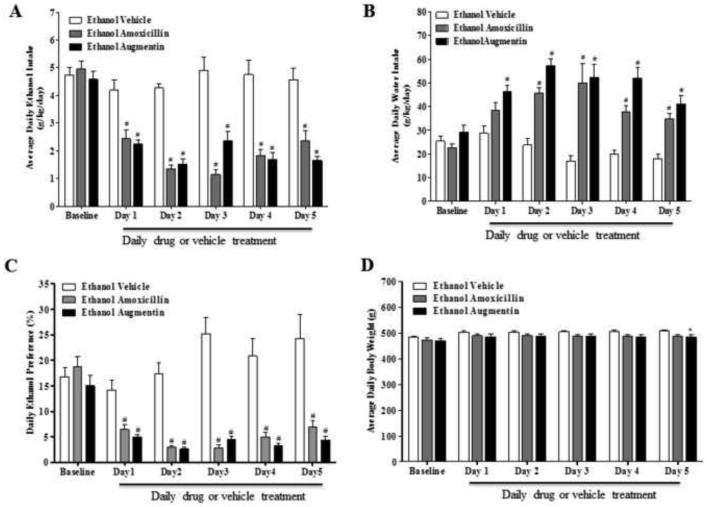
Figure 3.
(A) Effects of amoxicillin (AMOX) or Augmentin (AUG) on average daily ethanol intake (g/kg/day) in male P rats (n=12/β-lactam treatment group). A mixed ANOVA followed by Dunnett's t-tests revealed a significant reduction in ethanol intake by the AMOX and AUG treated groups starting on Test Day 1 and lasting through the end of the study as compared to the ethanol vehicle group. (B) Effects of AMOX and AUG on average daily water intake (g/kg/day) in male P rats. A mixed ANOVA followed by Dunnett's t-tests revealed a significant increase in water intake in AUG treated animals starting on Day 1 and lasting through the end of the study as compared to ethanol vehicle group; whereas the AMOX treated group had a significant increase in water intake, as compared to the ethanol vehicle group, starting on Day 2 and lasting though the end of the study. (C) Effects of AMOX and AUG on ethanol preference (%) in male P rats. A mixed ANOVA followed by Dunnett's t-tests revealed a significant decrease in ethanol preference in the AMOX and AUG treated groups starting on Day 1 and lasting through the end of the study as compared to the ethanol vehicle group. (D) Effects of AMOX and AUG on body weight in male P rats. A one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s t-test revealed no significant difference with AMOX treatment as compared to the ethanol vehicle group. However, Dunnett’s t-test revealed there was a very modest, but significant, difference in body weight of the AUG treated group as compared to the ethanol vehicle group on the 5th day of treatment. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. #, p<0.001; *, p<0.05.