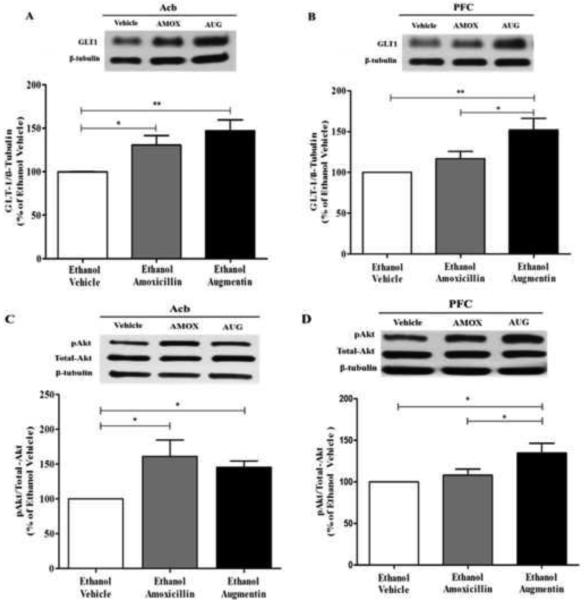
Figure 4.
Effects of amoxicillin (AMOX) and Augmentin (AUG) on GLT-1 and pAKT expression in Acb and mPFC of ethanol-experienced P rats (n=6/β-lactam treatment group). (A) There was a significant increase in Acb GLT-1 expression, of chronic ethanol consuming P rats, induced by AMOX and AUG, as compared to the ethanol naïve group (100%). (B) There was no significant upregulation of mPFC GLT-1 expression, of chronic ethanol consuming P rats, following AMOX treatment as compared to the ethanol vehicle group (100%). However there was a significant upregulation of mPFC GLT-1 expression following AUG treatment as compared to both the AMOX treated group and the ethanol vehicle group (100%). (C) As with Acb GLT-1 expression, both AMOX and AUG significantly upregulated Acb AKT phosphorylation in chronic ethanol consuming P rats. (D) As with mPFC GLT-1 expression, there was no significant upregulation of mPFC AKT phosphorylation in chronic ethanol consuming P rats following AMOX treatment as compared to the ethanol vehicle group (100%). However there was a significant upregulation of mPFC AKT phosphorylation in chronic ethanol consuming P rats following AUG treatment as compared to both the AMOX treated group and the ethanol vehicle group (100%). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01.