Figure 2.
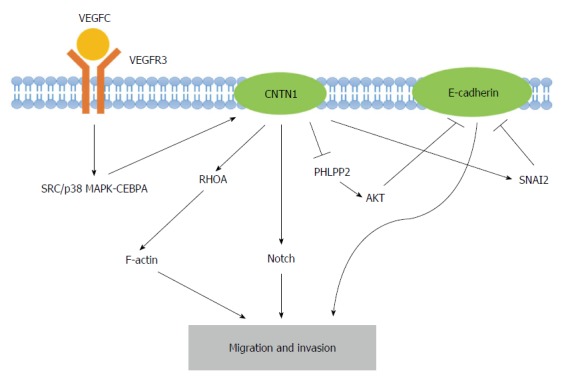
Graphic representation of the molecular mechanisms underlying the contactin 1-induced migration and invasion of cancer cells. Contactin 1 (CNTN1) serves as a downstream effector of the vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC)/FLT4 axis, which activates SRC/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-CEBPA signaling. CNTN1 regulates F-actin rearrangement with the aid of RhoA and activates Notch signaling. Furthermore, CNTN1 inhibits E-cadherin through the activation of SNAI2 as well as the upregulation of AKT, which result from the CNTN1-induced inhibition of PHLPP2. These mechanisms of CNTN1 contribute to the migration and invasion of cancer cells. PHLPP2: PH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase 2.
