Figure 2.
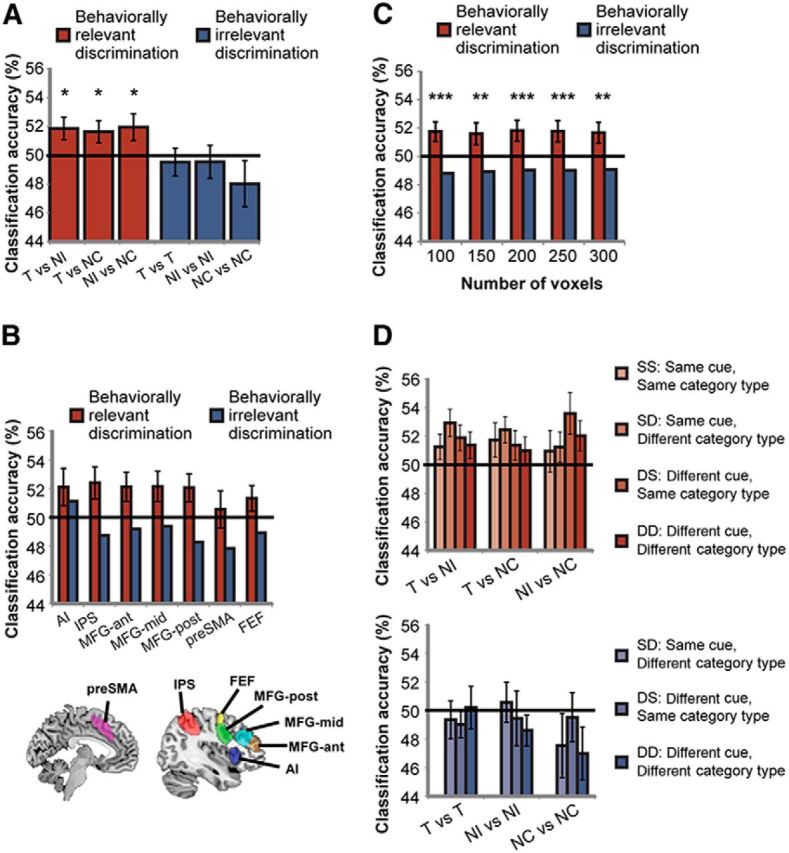
Behavioral relevance modulates categorical discrimination across the MD network. A, Categorical distinction that is behaviorally relevant is represented across the MD network, as measured by distributed neural pattern of activity (red bars). Distinction between categories that is behaviorally irrelevant is not well represented (blue bars). *p < 0.05. B, A similar pattern of activity is evident across all regions within the MD network. MD regions template is shown on sagittal and coronal planes. Error bars indicate SEM of the difference between behaviorally relevant and irrelevant discriminations in each region. C, Modulation of category discrimination by behavioral relevance in the MD system was robust across a large range of ROI sizes. Error bars indicate SEM of the difference between behaviorally relevant and irrelevant discriminations. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. D, Categorical discrimination is not modulated by aspects of the task that are orthogonal to the behavioral decision, such as cue and category type. Color coding of bars follows the classification matrix in Figure 1D. Error bars indicate SEM. AI, anterior insula; IPS, intraparietal sulcus; MFG-ant, middle frontal gyrus—anterior part; MFG-mid, middle frontal gyrus—middle part; MFG-post, middle frontal gyrus—posterior part; preSMA, presupplementary motor area; FEF, frontal eye field.
