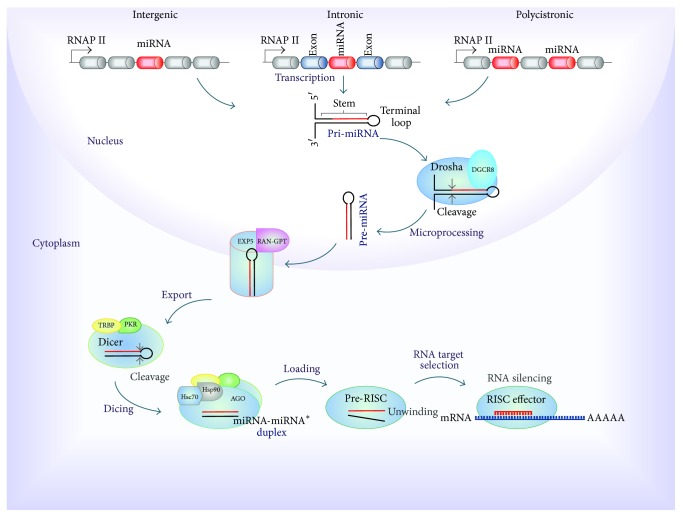
Figure 4.
Canonical pathway of miRNA biogenesis in human. miRNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) from intergenic, intronic, or polycistronic loci to long primary transcript, called primary miRNA (pri-miRNA), which consists in a stem, a terminal loop, and single-stranded RNA segments at both the 5′- and 3′-UTR sides. Microprocessor complex (Drosha and DGCR8 cofactor) cleaves the stem-loop and releases a small hairpin-shaped RNA, called precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA). Following, pre-miRNA is exported into the cytoplasm by the transport complex formed by protein exportin 5 (EXP5) and GTP-binding nuclear protein RAN-GTP. Subsequently, pre-miRNAs are cleaved by a ternary complex formed by Dicer, TAR RNA Binding Protein (TRBP), and Protein Activator of PKR (PACT), producing small RNA duplexes (miRNA-miRNA ∗). Next, these are loaded onto an Argonaute protein (AGO) to form an immature RNA-Induced Silencing Complex (RISC) or pre-RISC, in a process mediated for Heat shock cognate 70- (Hsc70-) Heat shock protein (Hsp90) chaperone complex. AGO protein separates the two strands to generate a mature RISC effector. Finally, RISC binds the target mRNA through complementary binding of 6 to 8 base pairs of the miRNA, with a specific sequence of the target resulting in the gene silencing.