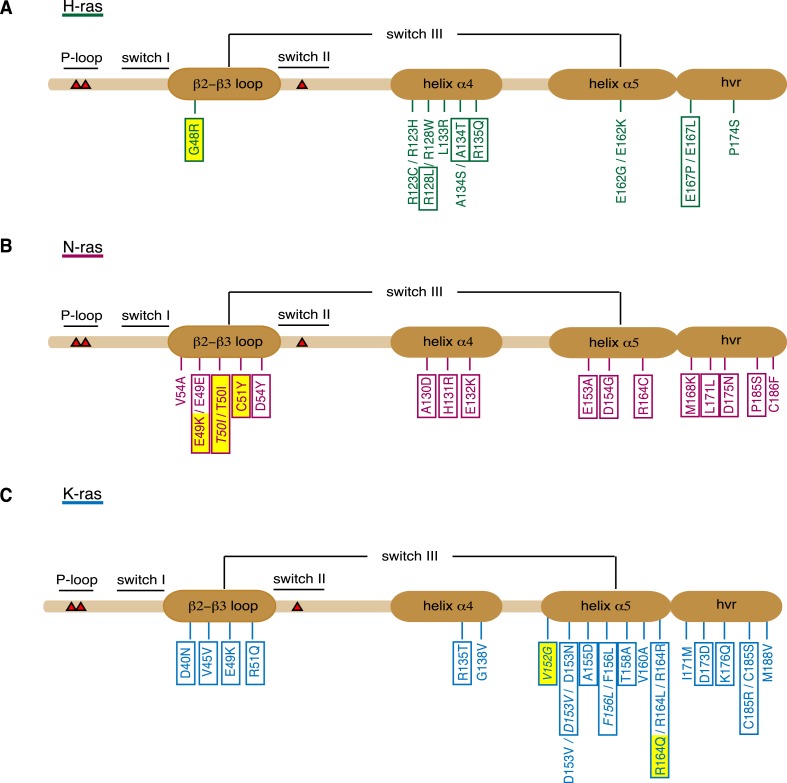
Figure 3. Orientation-switch III mutations in oncogenic Ras isoforms that are reported in cancer genome databases.
Cancer-associated point mutations (missense, nonsense, and silent) in the orientation-switch III regions as reported in COSMIC, cBioPortal, and ICGC databases. Schematic representations of the linear protein structures of (A) H-ras, (B) N-ras, and (C) K-ras. Critical functional regions in the structures are annotated; those of the orientation-switch III by ovals. Approximate position of hot-spot mutation residues (G12, G13, and Q61) is marked with red triangles. Mutations from cancer patient samples are boxed, RASopathy mutations are boxed and in italics, other annotated mutations are from cancer cell lines (Prior et al., 2012). Mutations that are studied here are highlighted in yellow. See also Figure 3—figure supplement 1.