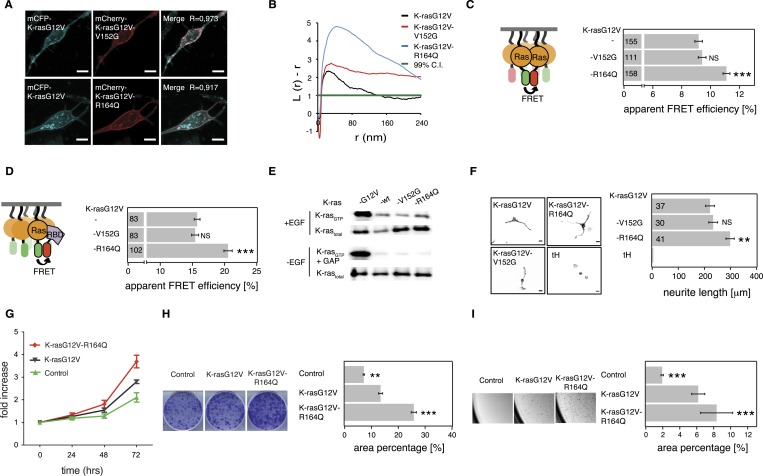
Figure 6. K-ras with colorectal cancer-associated mutation R164Q displays increased nanoclustering to drive oncogenic transformation.
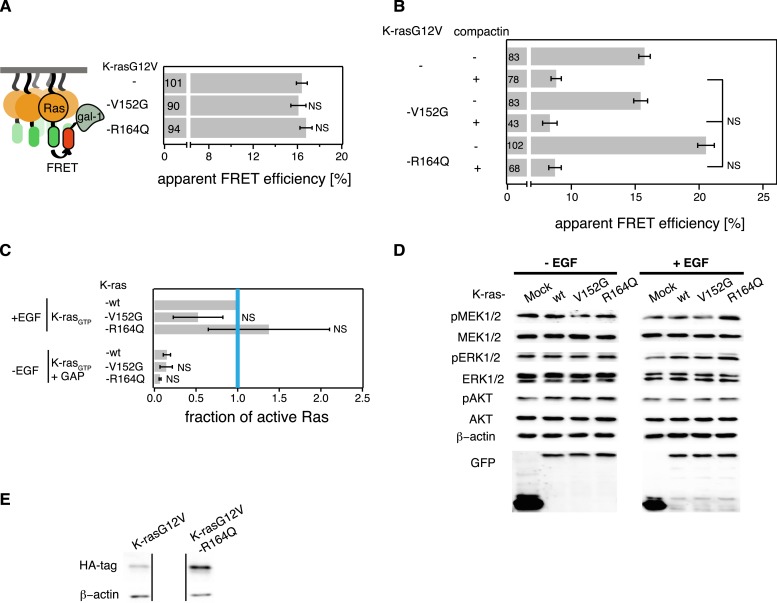
(A) Colocalization of mCFP-K-rasG12V and switch III mutants mCherry-K-rasG12V-V152G and mCherry-K-rasG12V-R164Q in BHK cells. The Manders' coefficient (R) that quantifies colocalization is marked on the merged images. Scale bar is 10 μm. (B) Electron microscopic nanoclustering analysis of BHK cells expressing indicated mGFP-tagged K-ras mutants. Normalized univariate K-functions, where maximal L(r)-r values above the 99% CI for complete spatial randomness indicate clustering at that value of r (number of membrane sheets analyzed per condition, n > 15). (C) The nanoclustering-FRET response of K-rasG12V-V152G, K-rasG12V-R164Q as compared to their parent construct in BHK cells. (D) RBD-recruitment FRET analysis of K-rasG12V-V152G, K-rasG12V-R164Q as compared to their parent construct in BHK cells. (E) RBD-pulldown experiments in BHK cells transiently expressing indicated K-ras mutants or (wild-type) wt K-ras. Top panel shows level of active K-ras after EGF-stimulation (100 ng/ml). Bottom panel shows GAP-sensitivity of wt and mutant K-ras proteins. (F) MAPK-dependent PC12 differentiation assay. Cells transiently expressed indicated mGFP-tagged K-rasG12V with or without mutations V152G and R164Q, or the control tH for 48 hr. Subsequently neurite length was assessed (left). Examples of confocal images of PC-12 cells expressing indicated constructs used for quantification (right). Scale bar is 15 μm. (C, D, F) Numbers in bars give number of analyzed cells from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (±SEM). Statistical analysis was performed as described in the ‘Materials and methods’ (NS, non-significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). (G) Proliferation of NIH/3T3 cells stably expressing K-rasG12V, K-rasG12V-R164Q, or a control construct for 72 hr. Control is transduced with the GFP reporter only. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (±SEM). (H) Transformation assay of NIH/3T3 cells virally transduced to stably express-indicated constructs and a GFP reporter. Foci formed after 7 days of growth were stained with crystal violet and mean (±SEM) foci areas from three biological repeats were quantified (right). Representative images of crystal violet stained foci of transduced NIH/3T3 cells (left). (I) Anchorage-independent growth of NIH/3T3 cells stably expressing K-rasG12V as compared to K-rasG12V-R164Q or a vector-only control. Colonies were imaged after 14 days (left), and the colony area was determined (right). Three independent biological repeats were performed, and each repeat was done in triplicate. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (±SEM). See also Figure 6—figure supplement 1.