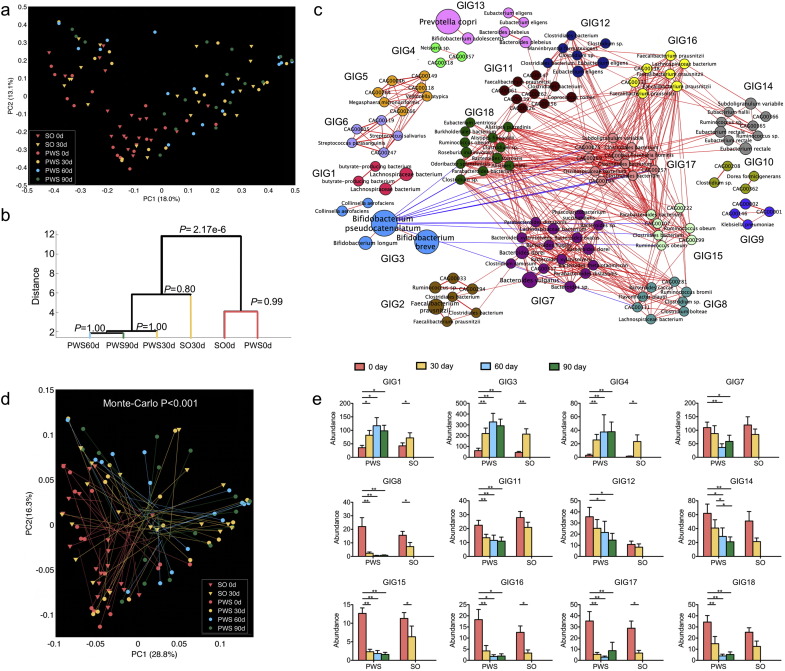
Fig. 3.
Concordance of structural shifts of gut microbiota and the improvement of the host metabolic health. (a) PCoA based on Bray–Curtis distance of all the 376 bacterial CAGs during the dietary intervention. (b) Clustering of gut microbiota based on distances between different groups calculated with MANOVA test of first 23 PCs (accounting for 80% of total variations) of PCoA based on Bray–Curtis distance of all bacterial CAGs. (c) Genome interaction groups interaction network. Network plot highlights correlation relationships between 18 GIGs of 161 prevalent bacterial CAGs at all time points from the two cohorts. Node size indicates the average abundance of the species/strains. Lines between nodes represent correlations between the nodes they connect, with line width indicating the correlation magnitude, and red and blue colors indicating positive and negative correlations, respectively. For clarity, only lines corresponding to correlations whose magnitude is greater than 0.5 are drawn, and unconnected nodes are omitted. (d) Procrustes analysis combining PCoA of GIGs (end of lines with solid symbols) with PCA of bioclinical variables presented in Fig. 1 (end of lines without solid symbols). For PWS, n = 17 at Day 0, 30, 60, and 90; For SO, n = 21 at Day 0 and n = 20 at Day 30. (e) Group level abundance shifts of GIGs that changed significantly during dietary intervention. Data are mean ± s.e.m. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test (two-tailed) was used to analyze variation between each two-time points in PWS or SO children. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.