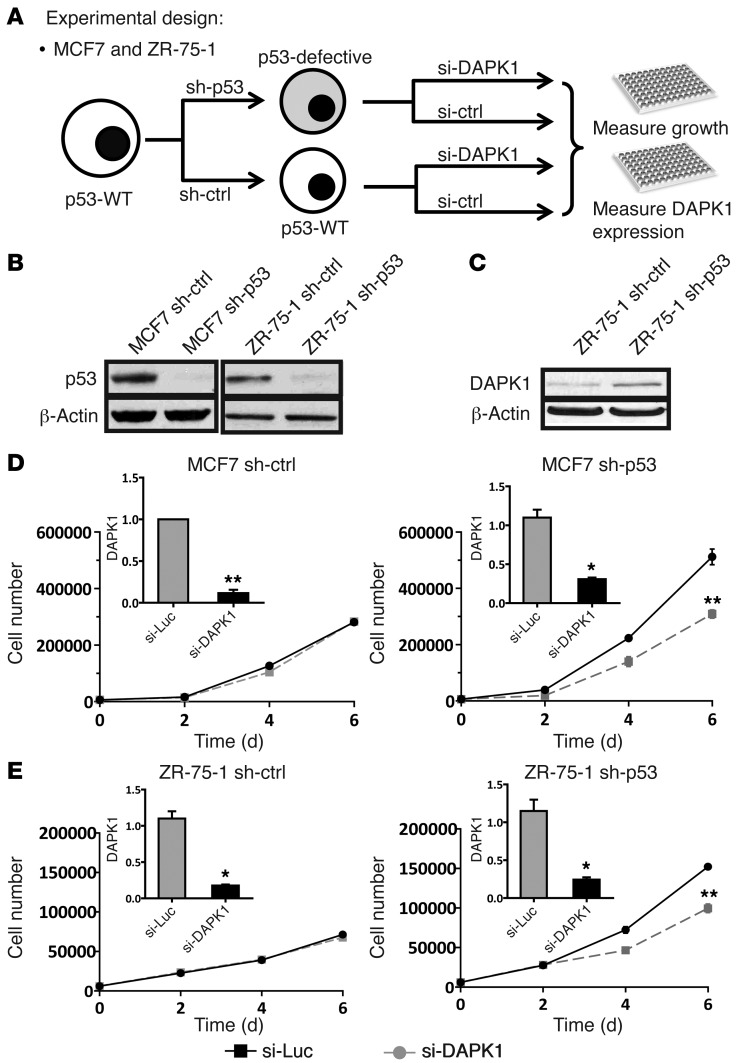
Figure 3. p53 depletion sensitizes p53-WT breast cancer cells to DAPK1 knockdown.
(A) Experimental design. In order to determine whether p53 status is relevant to cell line sensitivity to DAPK1 knockdown, we depleted p53 expression in 2 p53-WT cell lines (MCF7 and ZR-75-1) by constitutively expressing shRNA and comparing sensitivity to DAPK1 knockdown. (B) Shown is p53 protein expression in p53-WT and p53-depleted MCF7 (left panel) and ZR-75-1 (right panel) cells. (C) DAPK1 expression in p53-WT and p53-depleted ZR-75-1 cells. Western blot experiments were performed 3 times, and representative blots are shown. (D) Growth of MCF7 control (left panel) and MCF7 sh-p53 (MCF7 with p53 depleted; right panel) cells upon DAPK1 knockdown by siRNA. (E) Growth of ZR-75-1 control (left panel) and ZR-75-1 sh-p53 (ZR-75-1 with p53 depleted; right panel) upon DAPK1 knockdown by siRNA. DAPK1 knockdown and cell growth experiments were performed in triplicate, with results reported as average ± SEM. *P < 0.01; **P < 0.001, 2-tailed Student’s t test. sh-ctrl, MCF7 and ZR-75-1 cells transfected with empty vector; sh-p53, MCF7 and ZR-75-1 cells transfected with shRNA against p53 to make these cells p53 deficient.