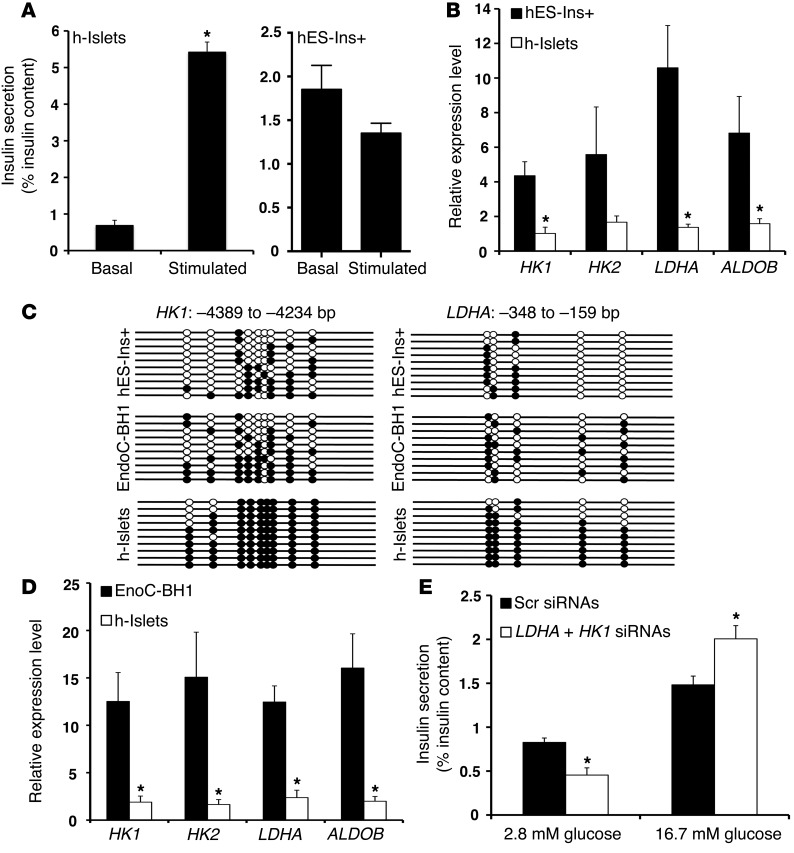
Figure 5. The metabolic programming directed by DNA methylation to regulate GSIS is conserved in human β cells.
(A) Static incubation GSIS assay, showing insulin secretion (percentage of insulin content) in differentiated insulin-positive (Ins+) human ES cells (hES-Ins+ cells; left panel), and human islets (h-islets; right panel) at 2.8 mM glucose and 16.7 mM glucose. (B) Relative mRNA expression of indicated genes in sorted GFP+ hES-Ins+ cells, compared with human islets from cadaveric donors (average donor age 43 years; n = 3). CYCLOPHILIN A was used as a housekeeping gene. The error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.05. (C) Bisulfite sequencing analysis for the HK1 and LDHA loci at indicated regions comparing sorted GFP+ hES-Ins+ cells, and EndoC-BH1 human β cell line, compared with human islets from cadaveric donors (representative clones from n = 3 samples per group). Each horizontal line with dots is an independent clone These regions are almost fully DNA methylated (filled circles) in human islets but largely hypomethylated (open circles) in hES-Ins+ cells and the EndoC-BH1 human β cell line. (D) Relative mRNA expression of indicated genes in EndoC-BH1 human β cell line, compared with human islets from cadaveric donors (average donor age 43 years). CYCLOPHILIN A was used as a housekeeping gene. n = 3 independent experiments. The error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.05. (E) Static incubation GSIS assay, showing insulin secretion (percentage of insulin content) in comparing EndoCBH1 cells treated with either a combination of siRNAs targeting HK1 and LDHA, or a scrambled (Scr) siRNA, at 2.8 mM glucose and 16.7 mM glucose. (n = 3). Error bars indicate ± SEM, *P < 0.05, Student’s t test.