Fig. 5.
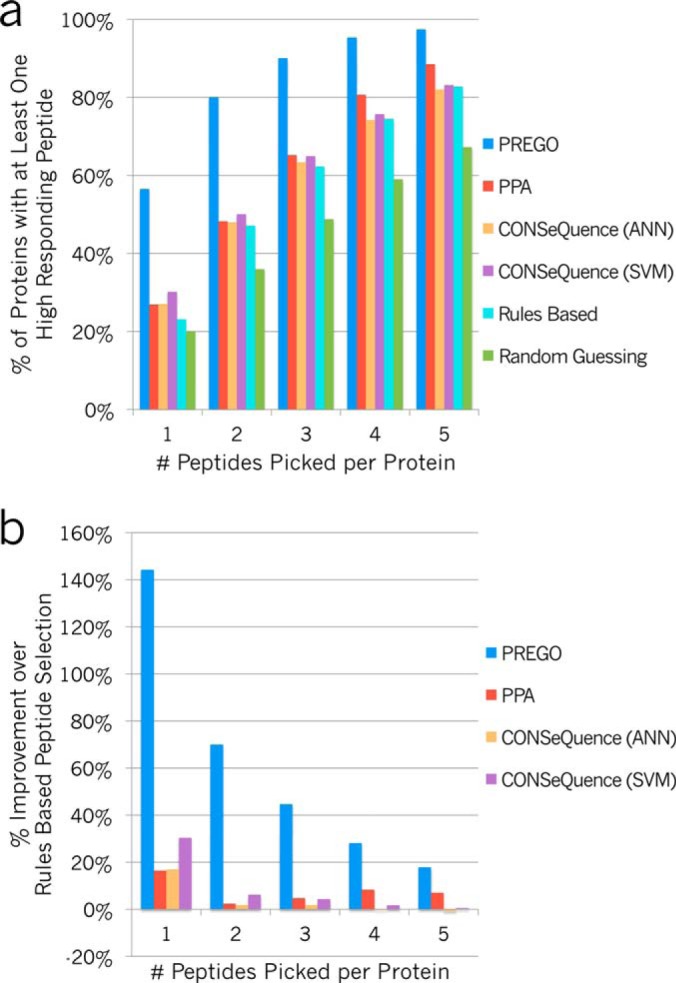
Percentage of proteins with at least one high-responding peptide, given N peptides picked. A, PREGO (blue), PPA (red), CONSeQuence artificial neural network (ANN, orange), and support vector machine (SVM, purple) machine learning-based scorers are compared with randomly guessing to select peptides (green) and the simple scoring function described in Equation 2 (cyan) based on common rules in the literature. Scorers are graded based on the likelihood that for any given protein, they could predict at least one high-responding peptide given N guesses. This is analogous to the strategy of picking N peptides to produce at least one useful peptide for each protein. For example, in Fig. 3 the top 1–5 peptides picked in CASZ1 have red borders and the high-responding peptides are shaded in blue. B, The same four learning-based scorers as a percentage improvement over rules based peptide selection. PREGO is dramatically better than the other approaches tested here at predicting high-responding peptides given five or fewer chances. All scoring data is based on the Stergachis et al. SRM testing data set.
