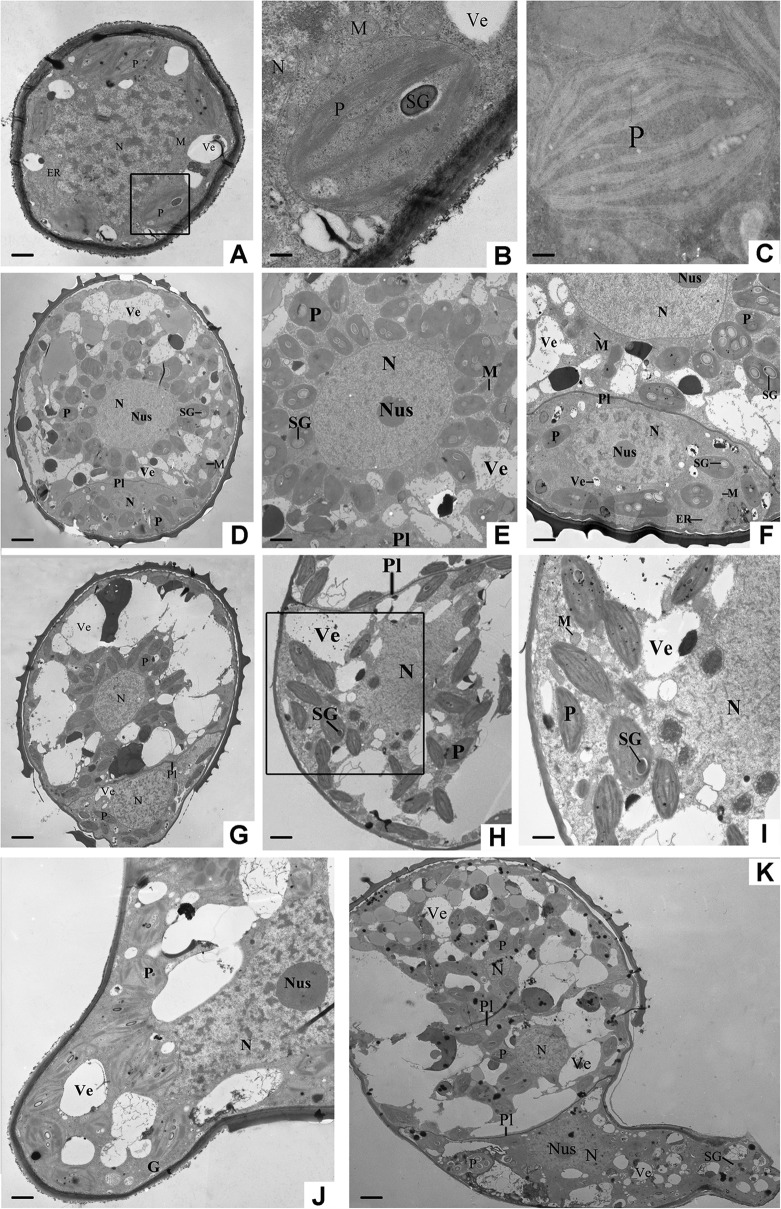
Fig. 3.
Ultrastructure of germinating spores from O. cinnamomea L. var. asiatica. A, Rehydrated spores (RSs), bar = 1 μm. B, Partial magnification of the circled area in A, showing chloroplasts and starch grains, bar = 0.2 μm. C, Plastid in RSs, bar = 0.2 μm. D, Double-celled spores (DCSs), bar = 3.2 μm. E, The large cell of DCSs, showing the nucleus and plastids, bar = 1.8 μm. F, The small cell of DCSs, bar = 1.25 μm. G, Germinated spores (GSs), bar = 3.2 μm. H, The large cell of GSs, showing the nucleus, plastids, and vesicles, bar = 1.8 μm. I, Partial magnification of circled area in H, bar = 0.8 μm. J, Small cell elongation image of GSs, bar = 1.25 μm. K, Overview of the spores with protonemal cells, bar = 3 μm. ER, Endoplasmic reticulum; G, Golgi body; M, Mitochondria; N, Nucleus; Nus, Nucleolus; P, Plastid; Pl, Plasmalemma; SG, Starch grain; Ve, Vesicle.