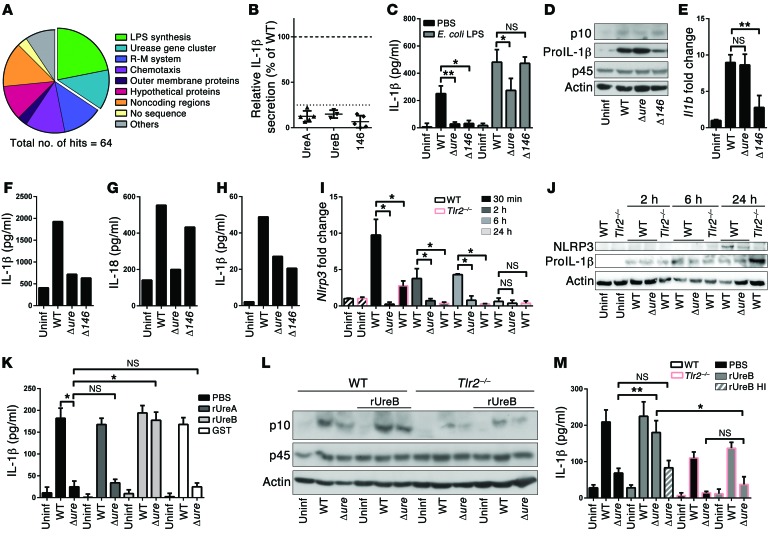
Figure 2. IL-1β secretion upon H. pylori infection requires LPS-induced transcriptional activation of pro–IL-1β and urease- and TLR2-dependent expression of NLRP3.
(A) Genome-wide screening for H. pylori tn mutants incapable of IL-1β secretion identifies the indicated mutant categories. R-M, restriction modification. (B) Relative IL-1β secretion of individual tn clones with insertions in ureA, ureB, and HPG27_146. (C–E and I–M) Murine BMDCs, (F and G) splenic CD11c+ DCs, and (H) human blood-derived DCs were infected overnight or for the indicated time points with G27 WT, Δure, or Δ146 strains of H. pylori and analyzed by (C, F, H, K, and M) IL-1β ELISA; (G) IL-18 ELISA; (D, J, and L) CASP1 p10 and p45, pro–IL-1β, and NLRP3 Western blotting; and (E and I) qRT-PCR (normalized to Gapdh and to uninfected controls). BMDCs were prestimulated with E. coli LPS where indicated, and 1 μg/ml recombinant GST-tagged UreA, UreB (native or heat-inactivated [HI] for 10 minutes at 70°C), or GST was added to cocultures as noted. Pooled data from 3 to 4 independent experiments are show in C, E, I, K, and M; a representative of 2 experiments is shown in F–H. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, Mann-Whitney U test. Error bars represent mean + SD.