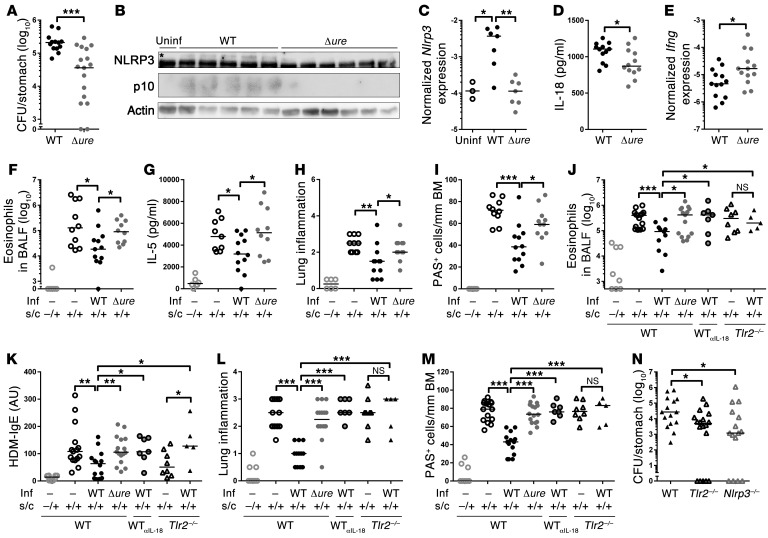
Figure 3. H. pylori urease is required for CASP1 activation, persistence, and asthma protection in neonatally infected mice.
(A–E) Neonatal C57BL/6 mice were infected for 1 month with WT or Δure H. pylori PMSS1 and assessed with respect to (A) gastric colonization, (B) gastric mucosal NLRP3 and CASP1 (asterisk indicates the NLRP3-specific band), (C) Nlrp3 expression, (D) IL-18, and (E) Ifng expression, as analyzed by (B) Western blotting, (D) ELISA, and/or (C and E) qRT-PCR. (F–M) Neonatally infected mice were additionally sensitized and challenged (s.c.) with (F–I) ovalbumin or (J–M) house dust mite (HDM) allergen starting at 4 weeks after infection to induce allergic asthma; αIL-18 mAb was administered weekly starting at the time of infection. Inf, infection. (F and J) Eosinophils in 1 ml of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). (G) IL-5 ELISA of ovalbumin-restimulated lung single cell preparations. (H and L) Lung inflammation, as assessed on H&E-stained sections. (I and M) Goblet cell metaplasia, as quantified on PAS-stained sections. BM, basement membrane. (K) House dust mite–specific serum IgE, as determined by ELISA. (N) H. pylori colonization of WT, Tlr2–/–, and Nlrp3–/– mice 1 month after infection. Symbols represent individual animals, and horizontal lines indicate the medians. Pooled data from 2 (A–E and N) and 3 (F–M) independent experiments are shown. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, Mann-Whitney U test.