Figure 4.
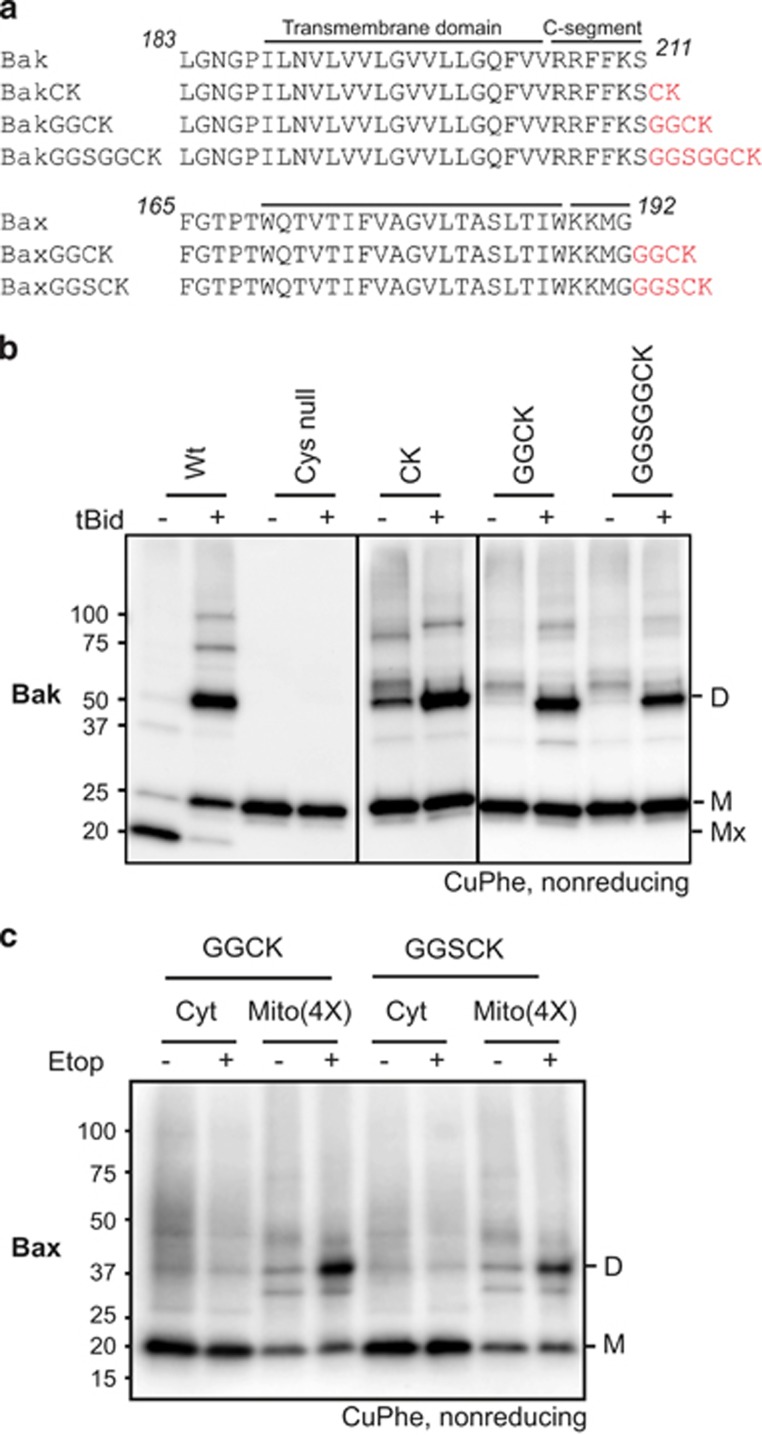
Extensions to the C-segments of Bak and Bax can be linked only after Bak and Bax are activated. (a) Extensions to the C-segments. Extra residues (red) added to Bak and Bax contain cysteine to monitor linkage, glycine to provide flexibility, and lysine to encourage targeting and insertion into the MOM. (b) C-segment extensions to Bak can be linked after but not before apoptosis. Membrane fractions from Bak−/−Bax−/− MEFs expressing the indicated C-segment variants were incubated without or with tBid prior to treatment with CuPhe. Samples were analyzed as in Figure 3a. Mx indicates an intramolecular cysteine disulfide bond (C14:C166) in nonactivated wt Bak. Note that in the absence of tBid, some linkage to other mitochondrial proteins was evident (Figure 4b), as observed for the nearby V205C (Figure 3a). Note also that some degree of linkage routinely occurred in the CK variant, suggesting that this variant may be arranged a little differently to other variants prior to its activation. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (c) C-segment extensions to Bax can be linked after but not before apoptosis. Bak−/−Bax−/− MEFs expressing the indicated C-segment variants were cultured in the presence of etoposide, and the cytosol (Cyt) and membrane (Mito) fractions incubated with CuPhe. The cytosol and fourfold-enriched membrane fractions were analyzed as in Figure 3a, but immunoblotted for Bax. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments