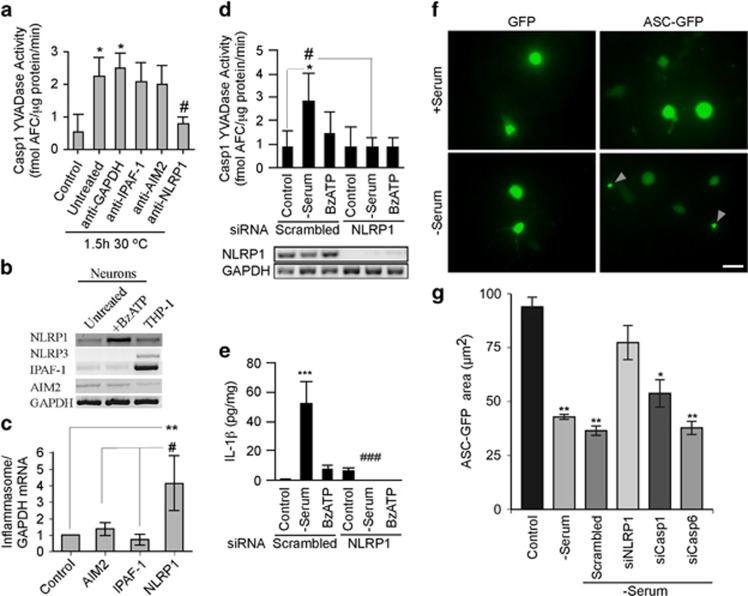
Figure 3.
The NLRP1 inflammasome activates Casp1 in serum-deprived and BzATP-treated human neurons. (a) Casp1 YVADase activity in S-100 extracts from neurons exposed to serum deprivation and treated with 1 μg/ml antibodies against IPAF-1, AIM2, NLRP1, or GAPDH. (b and c) Ethidium bromide agarose gel of RT-PCR amplicons (b) and qRT-PCR measurements (c) of NLRP1, NLRP3, IPAF-1, and AIM2 from untreated and 500 μM BzATP-treated neurons. Data represent the mean and S.E.M. of four independent neuron cell cultures. One-way ANOVA (P=0.0052) and Tukey–Kramer post hoc analysis (**P<0.01) compared with control, and #P<0.05 comparing NLRP1 with AIM2 and IPAF-1. (d) Casp1 YVADase activity in neurons treated with 1 μM scrambled or NLRP1 siRNA for 72 h followed by 30 min serum deprivation or 500 μM BzATP. Lower panel shows the effectiveness of the NLRP1 siRNAs knock down. Data represent mean and S.E.M. from four independent experiments. Repeated measures of ANOVA with a Tukey–Kramer post hoc analysis *P<0.05 comparing with control and #P<0.05 comparing pairs of scrambled versus NLRP1 siRNAs. (e) IL-1β levels from samples in d. ***P<0.001 compared with control and ###P<0.001 comparing siNLRP1 with scrambled siRNA. (f) ASC-GFP showing specks in serum-deprived primary human neurons. Bar represents 20 μm. (g) Quantitation of two individual preparations of human neurons. Statistics represent a multiple t-test compared with control. *P<0.05, **P<0.01