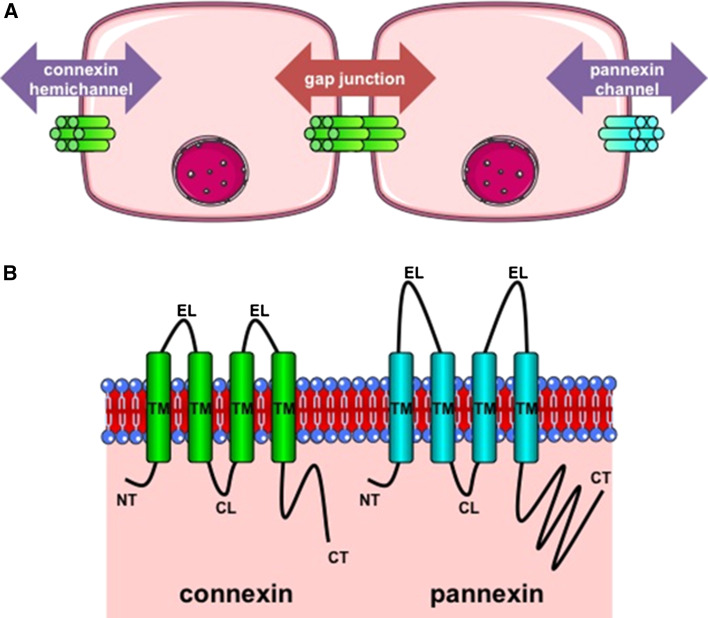
Fig. 1.
a Architecture of connexin and pannexin channels. Gap junctions are formed by the interaction between 2 hemichannels of adjacent cells and mediate intercellular communication (red arrow). Connexin hemichannels and pannexin channels are built up by 6 connexin proteins (green) and 6 pannexin proteins (blue), respectively, and support paracrine communication (purple). b Topology of connexin and pannexin proteins. Connexins (green) and pannexins (blue) all consist of 4 transmembrane domains (TM), 2 extracellular loops (EL), 1 cytoplasmic loop (CL), 1 cytoplasmic carboxy tail (CT) and cytoplasmic amino tail (NT). In comparison with connexins, pannexins have longer EL and CT areas