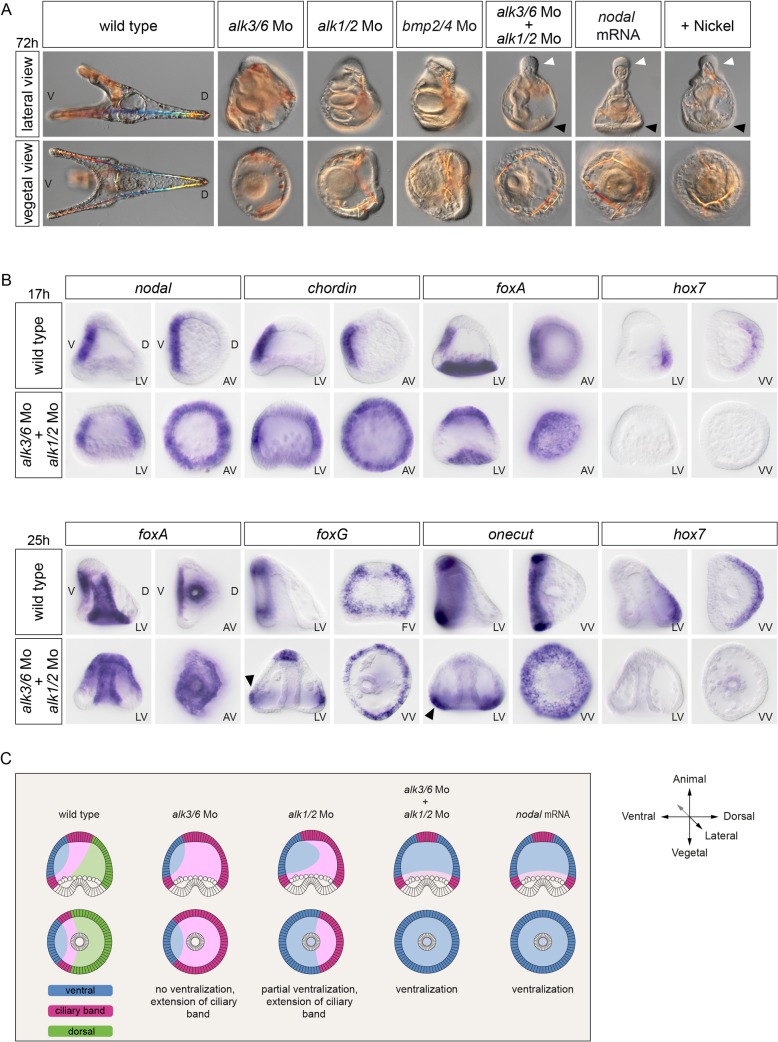
Fig 2. The double inactivation of alk1/2 and alk3/6 causes massive ectopic expression of nodal, resulting in extreme ventralization.
(A) Morphology of embryos at 72 hpf injected with morpholinos targeting either the alk3/6, alk1/2, or bmp2/4 transcripts or injected with a mixture of the alk1/2 and alk3/6 morpholinos. Simultaneous down-regulation of Alk1/2 and Alk3/6 caused a strong ventralization similar to that resulting from overexpression of nodal or from treatment with nickel chloride (a treatment that ventralizes sea urchin embryos by causing massive ectopic expression of nodal). Note the presence of a ciliary band in the vegetal pole region (black arrowheads) and the prominent proboscis (white arrowheads) in the animal pole region in the double alk1/2 + alk3/6 morphants and in nodal-overexpressing or nickel-treated embryos. (B) In situ hybridization on controls and alk1/2 + alk3/6 morphants at the blastula and gastrula stages with ventral, ciliary band, and dorsal marker genes. The strong ventralization of alk1/2 + alk3/6 morphants is presaged by the massive ectopic expression of nodal at blastula stages. Note the radial expression of the ciliary band markers foxG and onecut in the vegetal pole region of alk1/2 + alk3/6 morphants at the gastrula stage. (C) Scheme describing the changes in fate maps caused by the single or double inactivation of type I BMP receptors. In the simple alk3/6 knockdown, the ventral ectoderm remains unaffected and the dorsal ectoderm is converted into ciliary band, while in the alk1/2 morphants, the ventral ectoderm is expanded, giving rise to a partial ventralization. In contrast, in the double alk1/2 + alk3/6 morphants, the whole ectoderm is converted into ventral ectoderm. LV, lateral view; VV, vegetal pole view; AV, animal pole view; FV, frontal view; V, ventral; D, dorsal.