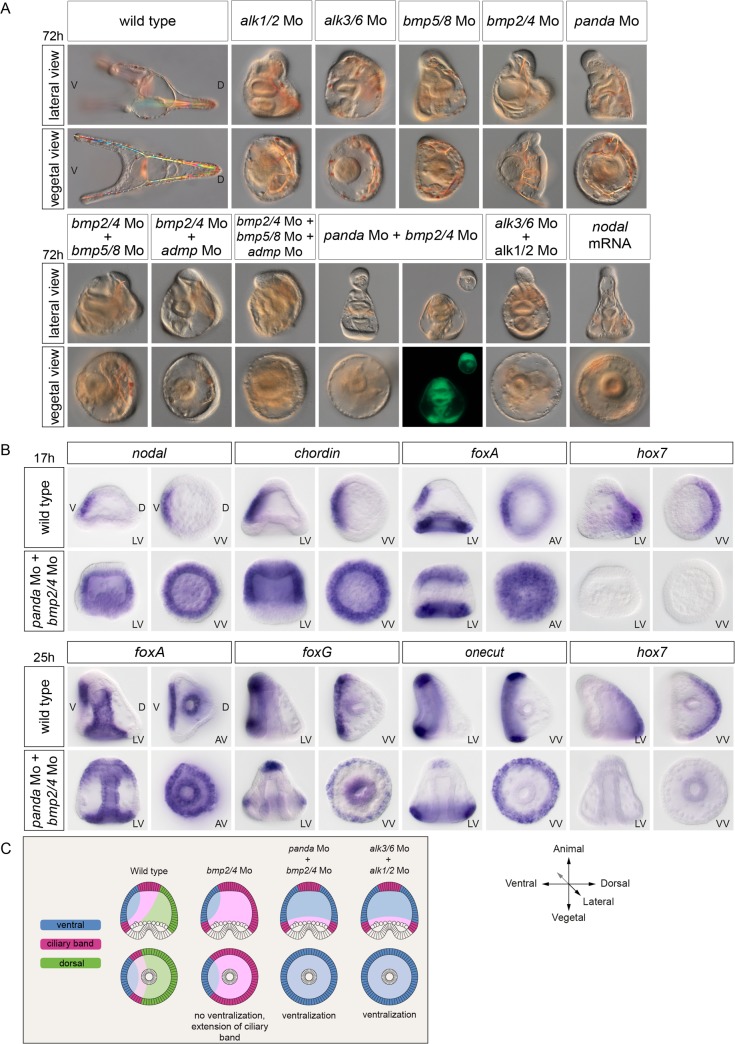
Fig 3. Panda is the TGF-β ligand that cooperates with BMP2/4 to restrict nodal during D/V patterning.
(A) Simple inactivation of alk1/2, alk3/6, bmp5/8, bmp2/4, panda, double inactivation of bmp5/8 +bmp2/4 or of bmp2/4 +admp, or triple inactivation of bmp2/4+ bmp5/8 + admp affects D/V polarity to various extents but does not cause full ventralization of the embryo. In contrast, double inactivation of panda and bmp2/4 causes an extreme ventralization of the embryo, mimicking the phenotype caused by nodal overexpression or by the double inactivation of alk1/2 and alk3/6. The ventralized phenotype of the double panda + bmp2/4 morphants is so strong that the proboscis in the animal pole frequently detaches from the rest of the embryo as a consequence of formation of a circular stomodeum. (B) In situ hybridization on controls and double panda + bmp2/4 morphants at the blastula and gastrula stages with ventral, ciliary band, and dorsal marker genes. Simultaneous inactivation of panda and bmp2/4 causes massive ectopic expression of nodal, suppresses dorsal marker gene expression, and restricts ciliary band markers to the vegetal pole, mimicking the effects of the double knockdown of Alk1/2 + Alk3/6. (C) Scheme describing the changes in fate maps caused by the single inactivation of bmp2/4, by the double inactivation of bmp2/4 and panda, or by the double inactivation of alk1/2 and alk3/6. LV, lateral view; VV, vegetal pole view; AV, animal pole view; V, ventral; D, dorsal.