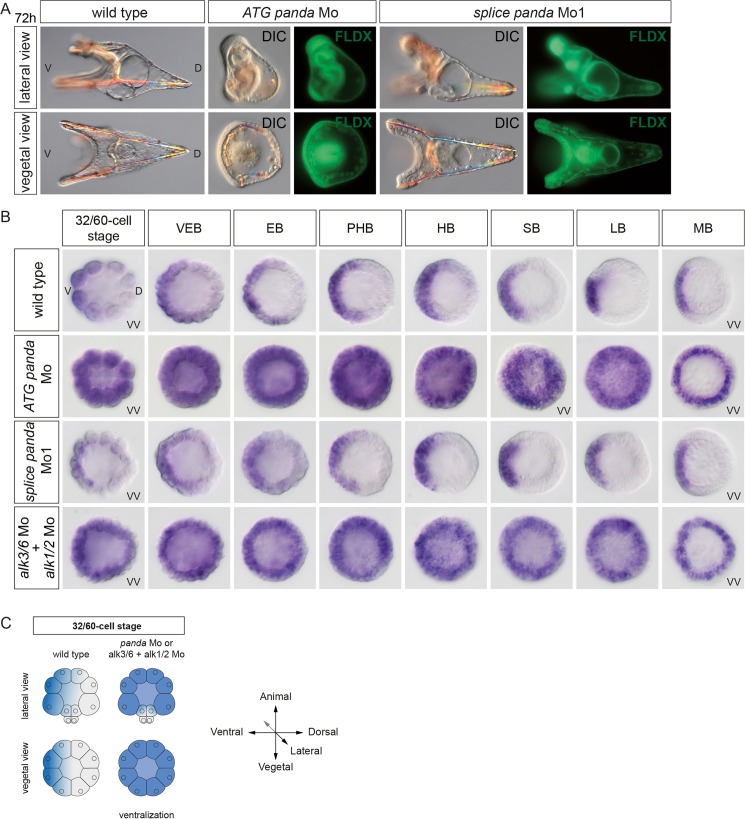
Fig 7. Maternal but not zygotic Panda function is required for the spatial restriction of nodal expression.
(A) Injection of a morpholino oligonucleotide targeting the translation start site of panda mRNA, but not of a morpholino targeting a splice junction, disrupts the establishment of D/V polarity. The lineage tracer Fluoresceinated Lysine-Fixable Dextran (FLDX) was coinjected with the morpholino. (B) In situ hybridizations against the nodal transcript at early stages. In the absence of maternal, but not of zygotic, Panda, a massive ectopic expression of nodal is observed starting at the 60-cell stage. Note that nodal expression remains radially expressed up to the mesenchyme blastula stage. Massive and early ectopic expression of nodal is also observed in the double alk1/2+alk3/6 morphants. VEB, very early blastula (about 120 cells); EB, early blastula (about 220 cells); PHB, prehatching blastula (about 300 cells); HB, hatching blastula (about 400 cells); SB, swimming blastula; LB, late blastula; MB, mesenchyme blastula. (C) Scheme summarizing the perturbations of nodal expression caused by blocking Panda or Alk1/2+Alk3/6. VV, vegetal pole view; V, ventral; D, dorsal.