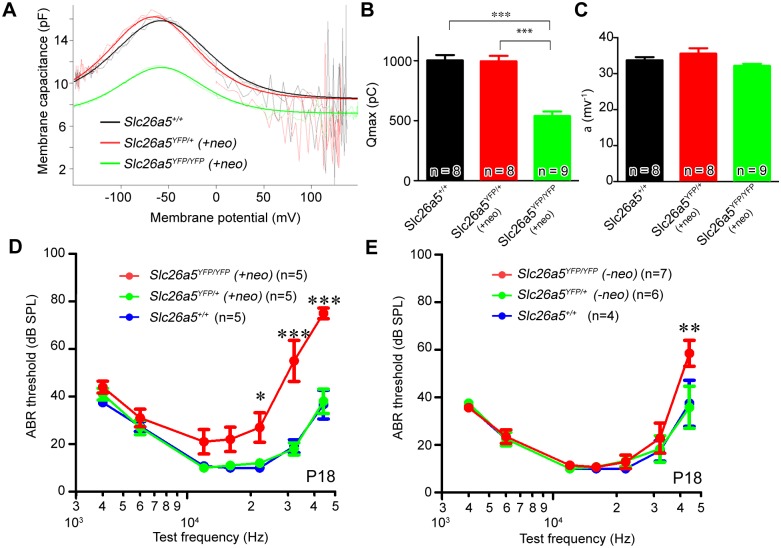
Fig 2. Slc26a5-YFP is functional in Slc26a5-YFP mice (+neo).
(A-C) NLC using isolated OHCs from Slc26a5 YFP/+ (+neo) mice at P20-P26. (A) NLC in isolated OHCs from Slc26a5 +/+ (black dotted lines), Slc26a5 YFP/+ (+neo) (red dotted lines), and Slc26a5 YFP/YFP (+neo) (green dotted lines) cochleae is shown. Smooth lines were obtained by fitting to a second order Boltzmann function where population Qmax and α are shown in (B) and (C) respectively. Black (Slc26a5 +/+), red (Slc26a5 YFP/+ (+neo)), and green (Slc26a5 YFP/YFP (+neo)) bars express the mean (± S.E.M.). Values are the mean ± S.E.M; (D) ABR thresholds of wildtype and Slc26a5-YFP (+neo) mice at P18 are similar (E) ABR thresholds of wildtype and Slc26a5-YFP (-neo) mice at P18 are similar. Values are the mean ± S.E.M.; ***: P<0.001, *: P<0.05 by two-way ANOVA followed by student's t test with a Bonferroni correction.