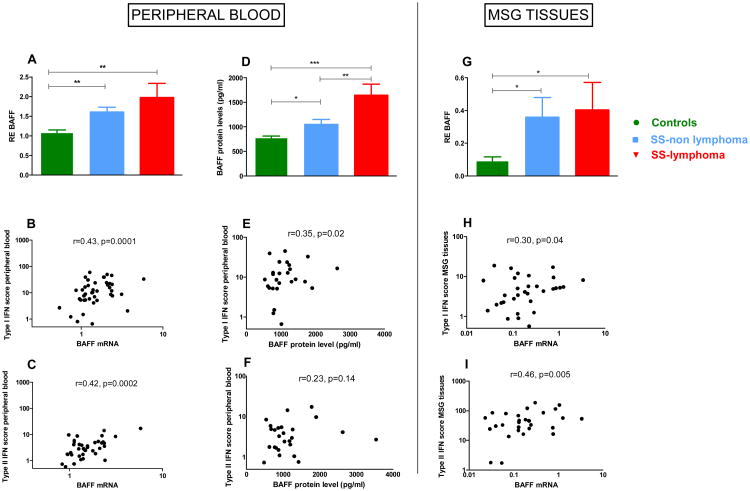
Fig.6. Association of type I and II IFN scores with B cell activating Factor (BAFF) mRNA expression and serum protein levels.
A. Normalized relative mRNA expression of the BAFF gene at the level of peripheral blood samples from 30 HC, 31 SS-non lymphoma and 13 SS-lymphoma patients. BAFF transcript levels were significantly increased in both SS subgroups complicated or non by lymphoma compared to HC (mean±SD: 1.97±1.32 vs 1.61±0.70 vs1.09±0.36, p-values: 0.005 and 0.002, respectively), with no significantly detectable difference between SS subgroups B. Peripheral blood BAFF mRNA transcripts were positively correlated with type I IFN score in SS patients (r=0.43, p=0.0001). C.. Peripheral blood BAFF mRNA transcripts were also positively correlated with type II IFN score in SS patients (r=0.44, p=0.0002). D. BAFF protein levels in serum samples from 24 HC, 62 SS-non lymphoma and 23 SS-lymphoma patients. SS-lymphoma patients had higher BAFF serum levels compared to both SS-non lymphoma and HC (mean ±SD: 1648.00±1178.00 pg/ml versus 1052.00±793.20 pg/ml versus 781.5±147.5 pg/ml, p-values: 0.002 and <0.0001, respectively), while SS-non lymphoma patients showed also increased serum BAFF levels compared to HC (p=0.03). E-F. A relatively weak correlation was observed between BAFF serum protein levels with peripheral blood type I IFN score (r=0.30, p-value=0.04), while type II IFN score was not correlated with BAFF serum levels in SS patients. G. BAFF normalized relative mRNA expression in MSG tissues from 17 SC, 31 SS-non lymphoma and 10 SS-lymphoma patients. BAFF mRNA levels were found to be increased in both SS subgroups complicated or not by lymphoma compared to SC (p-value: 0.02, for both comparisons). H-I. BAFF mRNA transcripts in MSG tissues were found to positively correlate with both type I and II IFN MSG tissue scores (r=0.3/ p-value =0.04 and r=0.46/ p-value=0.005, respectively). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, RE: Relative expression