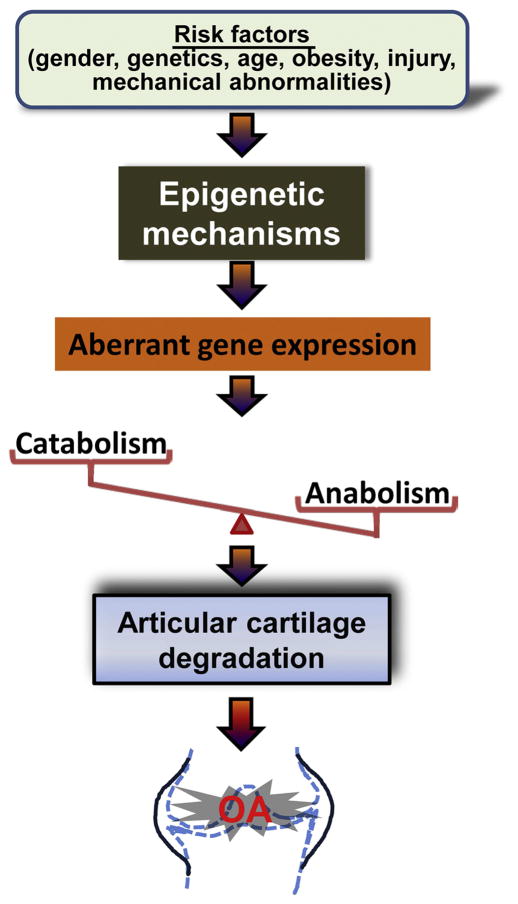
Figure 4.
Possible roles of epigenetic changes in the pathogenesis of OA. Under the accumulative effect of risk factors, chondrocytes undergo epigenetic events that result in aberrant expression of genes for specific transcription factors, cytokines, matrix-degrading proteinases, and ECM structural proteins in articular cartilage. Abnormal expression of these factors may disrupt the balance of catabolic and anabolic activities and compromise cartilage homeostasis, leading to articular cartilage degradation and the development of OA.