Figure 3.
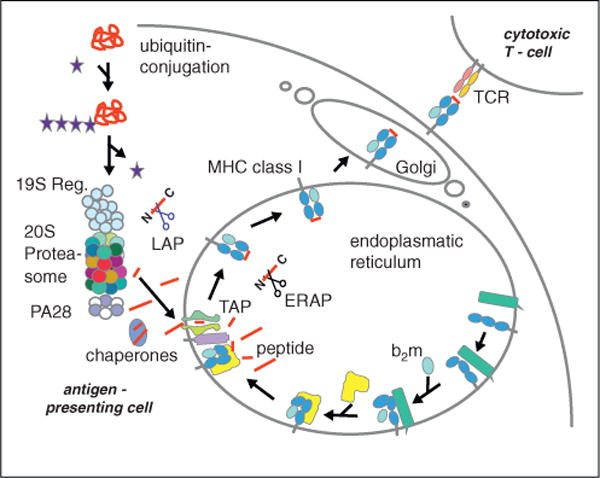
Antigen processing along the MHC class I pathway. Proteins synthesized in the cell are polyubiquitylated and degraded by the proteasome. Peptides produced are either of the ideal length for class I binding (8–9 amino acids) or are N-terminally extended precursors which can be cleaved by amino peptidases in the cytoplasm. The transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) transports the peptides into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) where they can be further trimmed by ER amino peptidase (ERAP)1/2. Peptides binding with high affinity to the MHC class I heavy chain/β2-microglobulin (b2m) complex induce a final folding and release from the ER lumenal chaperone calreticulin (in yellow) and the transmembrane chaperon calnexin (in green) to allow exit from the ER to the plasma membrane.
