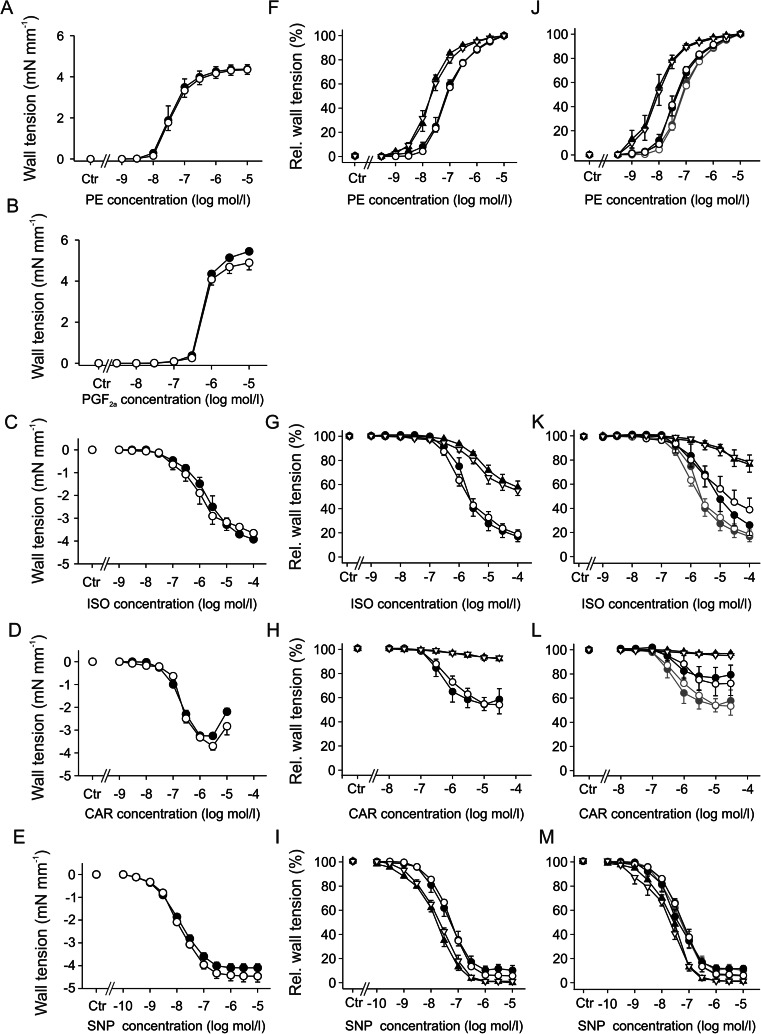
Fig. 3.
Cumulative drug-induced contractions and relaxations in wall tension of aortic rings (a–e), relative wall tensions after denudation (triangles) compared to intact aortae (circle) without (f–i) and with 1 week of chronic isoproterenol treatment (j–m) in Crem+/+ (open symbols) and Crem−/− (filled symbols) male mice. Curves in dark gray (j–m) show data of untreated aortae (f–i). The vascular tone was measured in response to stimulation with the α-adrenoceptor agonist phenylephrine (a, f, j; PE, n = 4–6) and prostaglandin F2α (b; PGF 2α, Crem+/+ n = 4, Crem−/− n = 3). Relaxations were induced after preconstriction with PE (1 μmol/l) by the β-adrenoceptor agonist isoproterenol (c, g, k; ISO; n = 4–6), the muscarinic receptor agonist carbachol (d, h, l; CAR; n = 5–8), and the nitric oxide donor sodium nitroprusside (e, i, m; SNP; n = 4–9). No significant differences between Crem+/+ and Crem−/− mice were observed