Fig. 19.
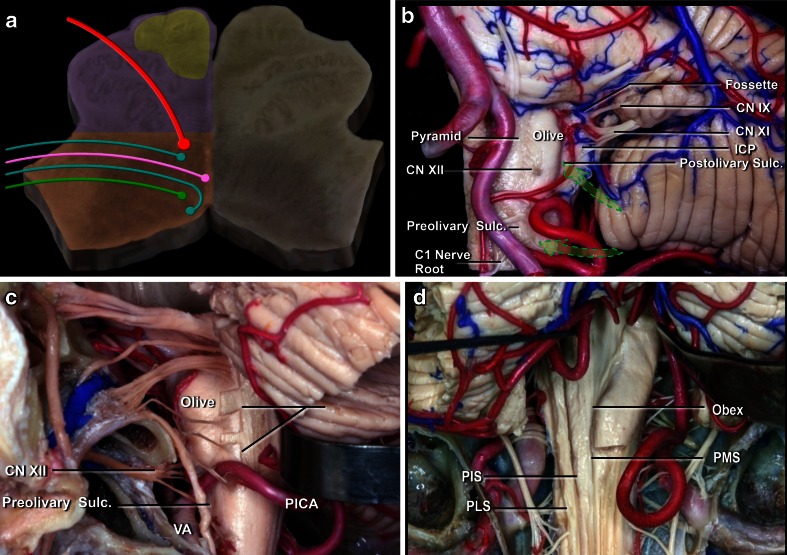
a Schematic representation of the medulla at the olive level, with the presence of the IX, X (green and pink), XI, and XII (red) cranial pairs nuclei and topography of the corticospinal tract (yellow), which is much nearer to the midline as compared to the pons and the midbrain. b Ventral medulla. The safe entry zones in the ventral medulla are the preolivary and postolivary sulci. The preolivary sulcus is located between the olive and the pyramid, which houses the CST. The depression rostral to the olive, the supraolivary fosette, is just below the junction of the facial and vestibulocochlear nerves with the brainstem. The glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves exit the medulla just dorsal to the postolivary sulcus, which is located between the olive and inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP). The hypoglossal rootlets exit the medulla along the preolivary sulcus. c The far lateral approach used for pre- and post-olivary sulci. d Dorsal medulla. The posterior median (PMS), intermediate (PIS), and posterolateral (PLS) sulci have been proposed as the safe entry zones. The suboccipital median approach