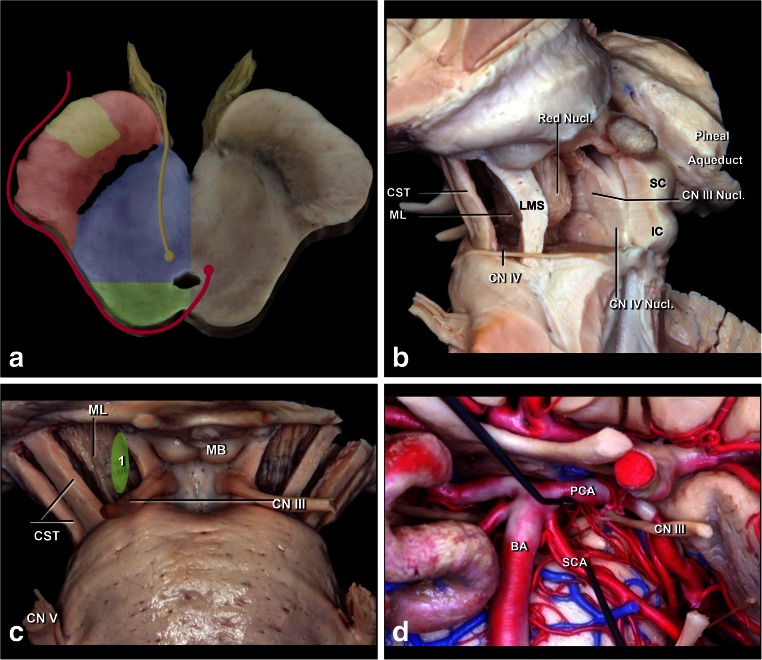
Fig. 2.
a Schematic representation of the midbrain at the level of the oculomotor nerve. The substantia nigra and medial lemniscus is the border between ventral (anterior) and central parts of the midbrain, while the level of the cerebral aqueduct is the border between central (blue) and dorsal (posterior) midbrain (green). The corticospinal tract (yellow) in the ventral midbrain (red); nuclei and courses of the CN III (yellow) and IV (red) in the central (blue) and dorsal midbrain. b Lateral view of the midbrain. The ventral (anterior) midbrain, which contains the corticospinal tract (CST), is situated in front of the medial lemniscus (ML) and substantia nigra. The central midbrain containing the red, oculomotor and trochlear nuclei is positioned between medial lemniscus and aqueduct. The dorsal (posterior) midbrain composed of superior (SC) and inferior colliculi (IC) is positioned behind the cerebral aqueduct. The nuclei of the CN III and IV are located just ventral to the aqueduct. c Anterior view of midbrain. 1 Perioculomotor entry zone is bordered medially by exit point of the CN III and laterally by the corticospinal tract (CST). d The perioculomotor zone is limited by the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) superiorly and by the superior cerebellar artery (SCA) inferiorly