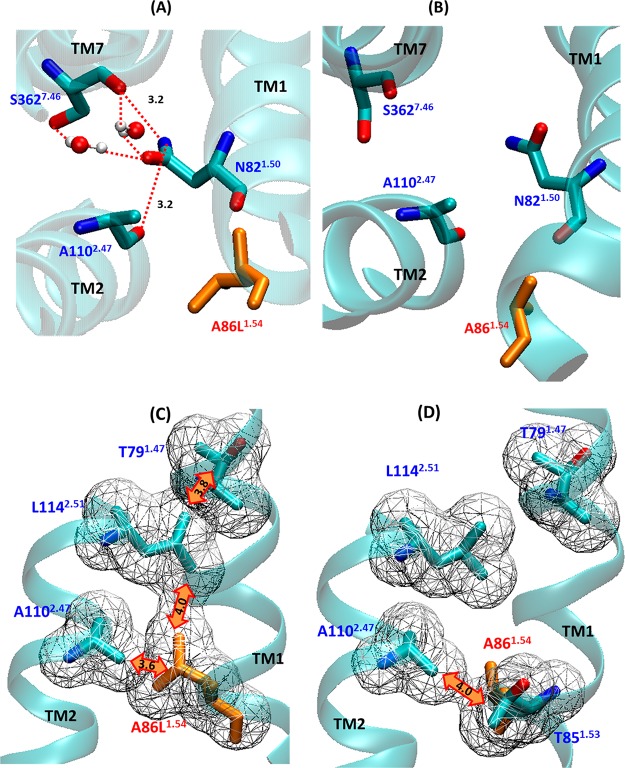
Figure 6.
Differences in the interhelical interaction due to the mutation A86L1.54. (A) The direct and indirect contacts of N821.50 with A1102.47 and S3627.46 in the vicinity of the A86L1.54 mutation in NTSR1-GW5 (B) and the wild type receptor. Two waters that have important roles in indirect contacts between N821.50 and S3627.46 were observed in 53 and 83% of the snapshots from MD simulation trajectories, respectively. (C and D) Hydrophobic interaction pattern near the A86L1.54 mutation in NTSR1-GW5 and wild type receptor. The T791.47–L1142.51 and A86L1.54–L1142.51 interactions in NTSR1-GW5 and T851.53–A1102.47 hydrophobic interaction in the wild type receptor are highlighted by orange double arrows. The van der Waals surfaces of the atoms are shown as mesh, and the distances shown in orange are in Å.