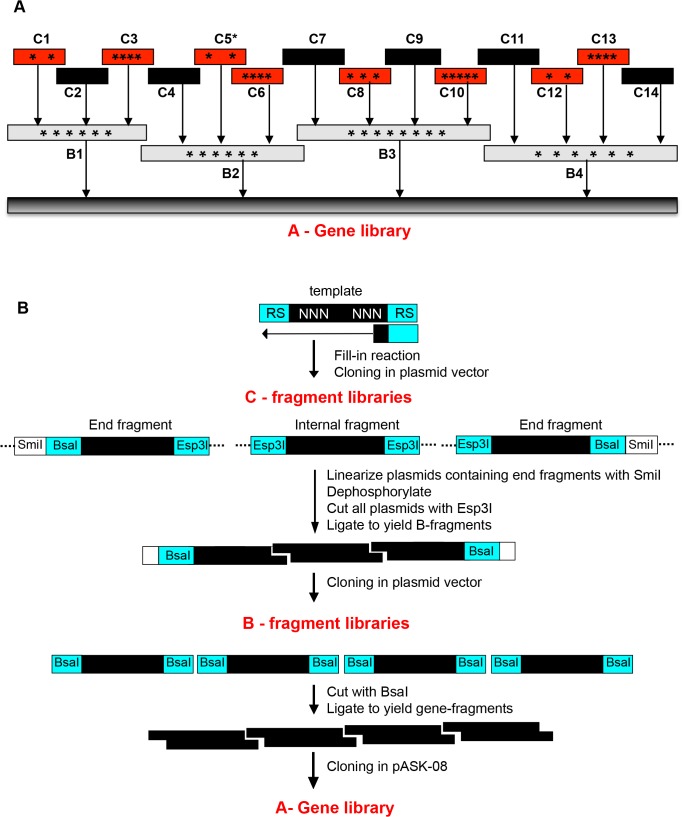
Fig 3. Modular division of thisF gene and hierarchical assembly scheme.
(A) The gene sequence was divided into 14 modules (C1-C14). The black bars represent modules with wild type sequence; the red bars represent randomized sequences. The modules were chemically synthesized and randomization, which was achieved by incorporating trinucleotide mixtures at the corresponding codon positions, indicated by asterisks. Module C5 was synthesized both as wild type and as randomized sequence. The gene library was generated by combinatorial assembly of smaller modules (fragment libraries) at two steps, schematically represented with arrows. (B) Enzymatic steps involved in generation of double-stranded fragments and step-wise gene assembly. All C-fragments were designed in such a way that recognition sequences of Type RII restriction enzymes are located outside the coding sequence and are removed in the act of cleavage, whereas cleavage points in both DNA strands are within coding sequence but outside randomized DNA sites. Also refer to Table 1.