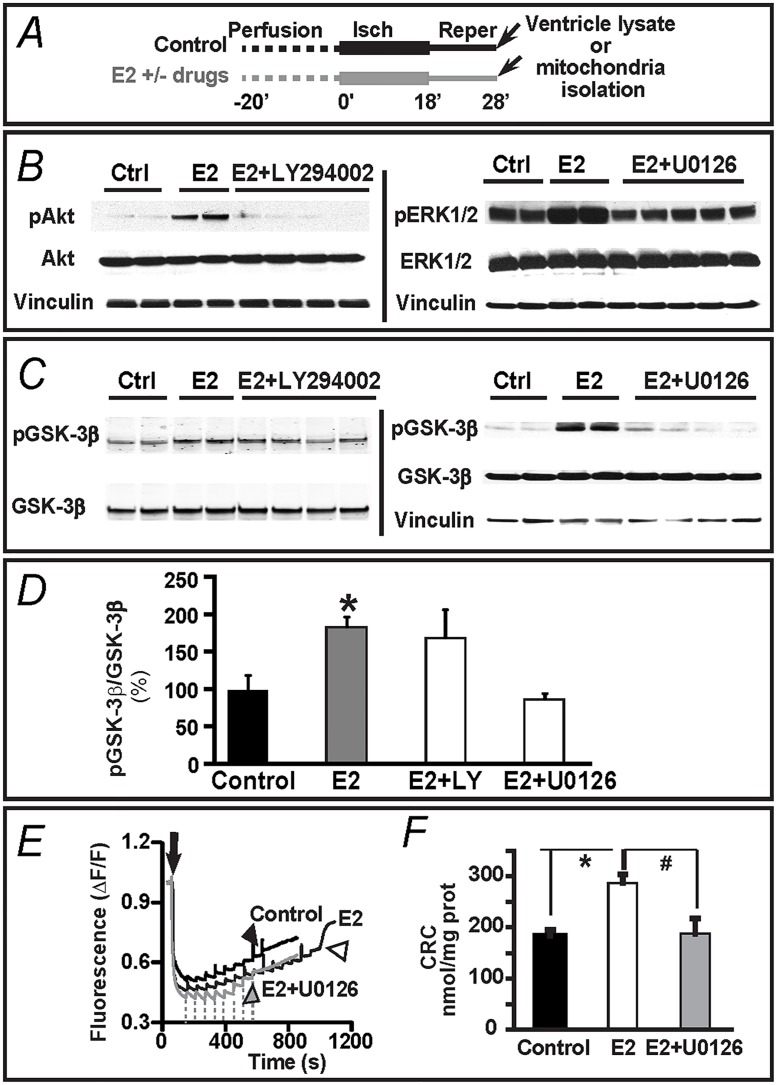
Fig 7. MEK1/2/ERK1/2 –but not PI-3K/Akt- signaling supports E2-mediated protection from I/R via GSK-3β and mPTP.
A. I/R protocol. Arrows mark the time of sample preparation. B. Immunoblots show that addition of the inhibitor of MEK1/2/ERK1,2 pathway, U0126 (1 μM) abolishes E2-induced up-regulation of pERK and the inhibitor of PI3-K/Akt pathway, LY294002 (10 μM) abolishes the increase in pAkt induced by 40 nM E2. C,D. Immunoblots and corresponding bar graphs show that the inhibitor of MEK1/2/ERK1,2 pathway, U0126 (1 μM)-but not the inhibitor of PI3-K/Akt pathway, LY294002 (10 μM)- abolishes the increase in pGSK-3β/GSK-3β ratio induced by 40 nM E2. E. Calcium load measurements were as indicated in Fig 5. Arrow, addition of mitochondria. Arrowheads, mark the massive Ca2+ release (an index of mPTP opening) in mitochondria from control (black), E2 (40 nM)-treated (open), and treated with E2 (40 nM) + U0126 (1 μM) (grey) hearts. Dashed lines mark the time of Ca2+ addition to the E2+U0126 treated sample. F. Mean values of calcium retention capacity (CRC) demonstrate that 1 μM U0126 prevents the beneficial effect of 40 nM E2. Note that vinculin was used as a loading housekeeping protein. All values were obtained from WT male mice and expressed as mean±SEM; * P<0.05 E2-treated group versus control; and # P<0.05 E2+U0126 versus E2-treated group (n = 5–7 hearts/group).