Figure 1.
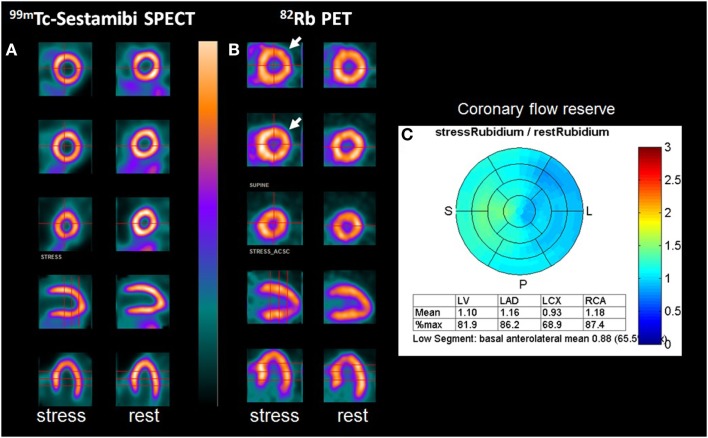
A 56-year-old woman with a history of obesity (BMI: 31.2 cm/kg2), hypertension, hyperlipemia, and type 2 diabetes complicated of retinopathy and renal failure. The patient was referred to the Nuclear Medicine department for detection of coronary artery disease and underwent both Tc-99m-sestamibi SPECT (D-SPECT, Spectrum Dynamics, Haifa) and rubidium-82 PET/CT (Discovery 690 VCT, GEMS, Buc, France) as part of a clinical trial. SPECT (93% of the predicted maximal heart rate, no symptoms, EKG positive) was normal with a homogeneous uptake of the tracer both at stress and at rest (A). 82Rb PET performed after Dipyridamole infusion showed a mild decrease of the tracer uptake in the lateral wall (arrow), completely reversible at rest, raising the suspicion of ischemia in the territory of the circumflex artery (B). This hypothesis was then confirmed by quantitative data derived from myocardial blood flow measurement with a coronary steal phenomenon in the same territory [coronary flow reserve (CFR) <1; (C)]. In addition, the CFR was markedly decreased (<1.5) in the territory of both the left descending artery and the right coronary artery, suggesting the presence of significant stenosis of these two coronary arteries. The coronary angiography confirmed the diagnosis of three-vessel disease and the patient underwent surgical revascularization. This case report underlines the greatest sensitivity of 82Rb PET over SPECT in the setting of balanced ischemia, in relation with the ability to perform absolute quantification of myocardial blood flow.