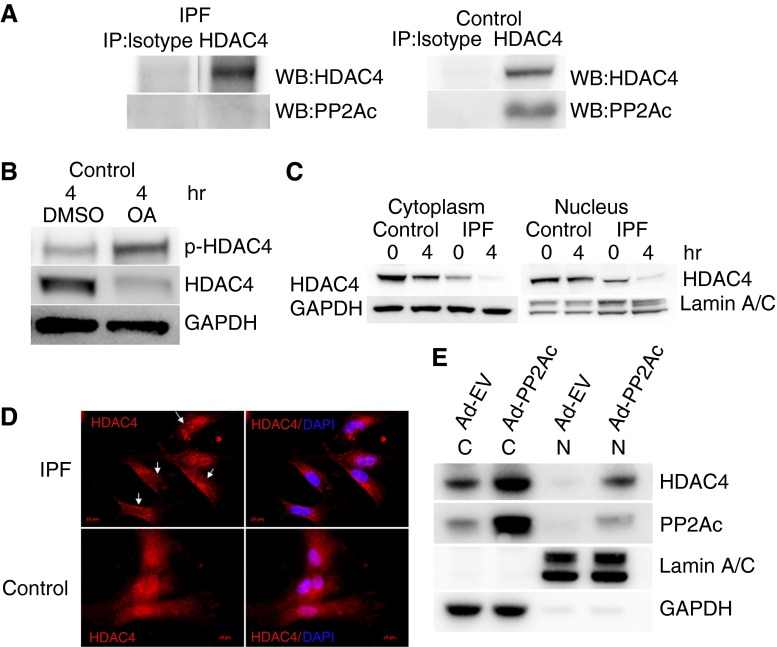
Figure 3.
Low protein phosphatase (PP) 2A in IPF fibroblasts results in HDAC4 hyperphosphorylation and decreases its nuclear localization. (A) IPF and control fibroblasts were plated on type I polymerized collagen for 4 hours. Immunoprecipitation of HDAC4 was performed, and samples were analyzed for association with PP2Ac. Immunoprecipitation with isotype antibody was used as a control. (B) Control lung fibroblasts were pretreated with the PP2A inhibitor okadaic acid (OA) (10 nM; 60 min) or DMSO as a control. The cells were then seeded on type I polymerized collagen matrices and phosphorylated, and HDAC4 protein expression was examined by Western blot analysis as a function of time. GAPDH is shown as a loading control. (C) IPF and control fibroblasts were seeded on polymerized collagen for 4 hours. The cells were lysed, and nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were analyzed for HDAC4 expression by Western blot analysis. Lamin A/C is shown as a nuclear loading control; GAPDH is shown as a cytoplasmic loading control. (D) IPF and control fibroblasts were seeded on polymerized type I collagen for 4 hours. The cells were stained with HDAC4 antibody conjugated with Cy-3. 4′6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) indicates nuclear staining. Arrows point to four IPF fibroblasts with low nuclear HDAC4 expression. (E) PP2Ac was overexpressed in IPF fibroblasts using an adenoviral vector containing a wild-type PP2Ac construct (Ad-PP2Ac). Cells infected with empty vector served as control (Ad-EV). The cells were seeded on polymerized collagen for 4 hours and then lysed. Nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions were analyzed for PP2Ac and HDAC4 expression by Western blot analysis. Lamin A/C is shown as a nuclear loading control; GAPDH is shown as a cytoplasmic loading control.