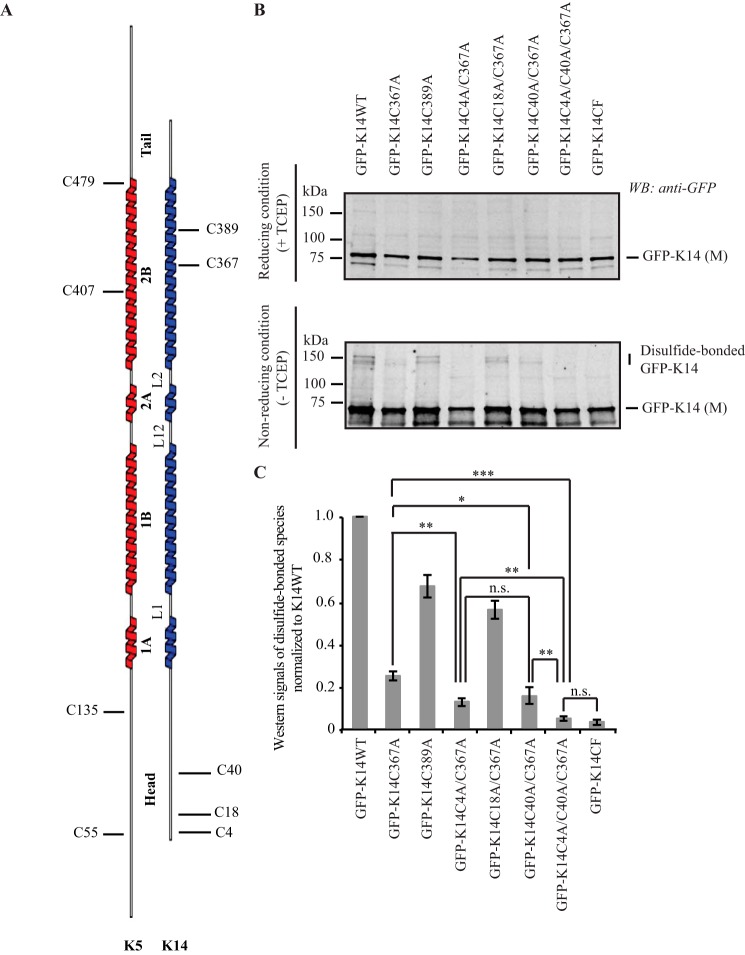
FIGURE 1.
K14 cysteine residues involved in disulfide bonding. A, schematic representation of the location of cysteine residues in human K5 and K14. B, immunoblotting analysis shows that replacing Cys in K14 with Ala at positions 4, 40, and 367 results in a complete loss of disulfide-bonded dimers of the GFP-K14 upon transfection in 308 mouse keratinocytes (top gel, reducing conditions (+TCEP); bottom gel, non-reducing conditions (−TCEP)). Reducing and non-reducing samples were loaded on SDS-PAGE and analyzed simultaneously using the same exposure time when scanned on the infrared imaging system (LI-COR Biosciences). C, quantification of disulfide-bonded species of GFP-K14WT and cysteine variants by densitometry-based analysis of Western signals of GFP-K14 as reported in B. n = 3 experiments were performed. Western signals of the TECP-treated GFP-K14 (monomer) as the loading control. Error bars, S.D. *, p < 0.5; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; n.s., not significant (p > 0.5).